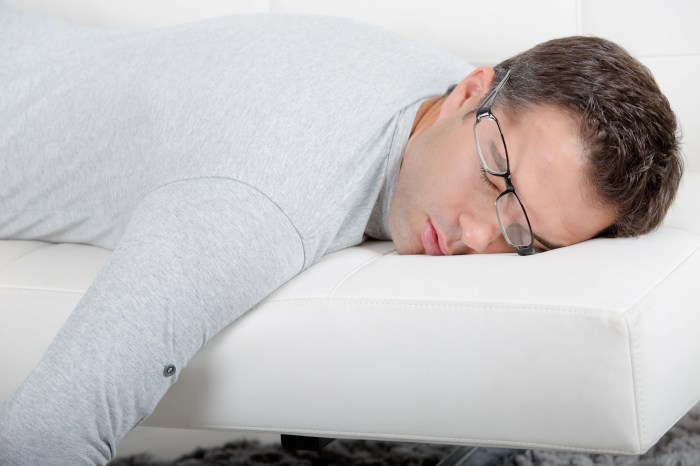
Fatigue symptoms causes diagnosis and treatment is a complex issue affecting many people. This in-depth exploration dives into the various facets of fatigue, from its different forms and potential causes to effective diagnostic methods and treatment strategies. Understanding the nuances of fatigue, including its physiological and psychological roots, is crucial. This article will explore the…
Author: Jonatan Bergnaum
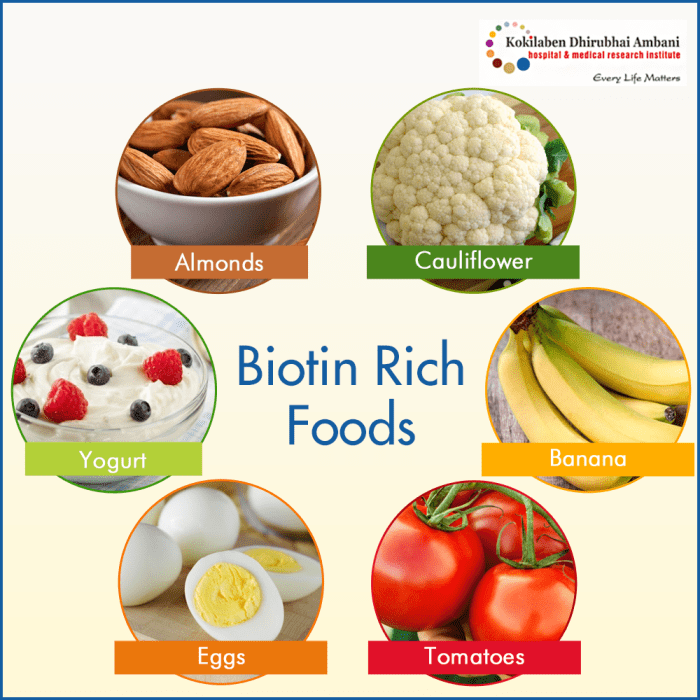
Biotin for Hair Growth A Deep Dive
Biotin for hair growth is a topic of considerable interest, and for good reason. This exploration delves into the fascinating world of biotin, examining its role in supporting not only healthy hair but also overall bodily functions. We’ll uncover the science behind biotin’s impact on hair follicle health, analyze supplementation strategies, and explore factors that…
Purified vs Distilled Water A Deep Dive
Purified vs distilled water is a common topic of debate, especially for those concerned about the quality of their drinking water. This in-depth look will explore the differences between these two types of water, examining their purification methods, chemical composition, health implications, applications, cost, environmental impact, and more. We’ll delve into the science behind each…
What Does Mouth Cancer Look Like? A Guide
What does mouth cancer look like? This introduction explores the often-overlooked visual characteristics of this serious condition. Understanding the early signs and symptoms is crucial for prompt detection and treatment. We’ll delve into the different types of oral cancer, their prevalence, and risk factors. Crucially, we’ll look at how to identify cancerous lesions, differentiating them…
Skin Boils Picture Gallery Visual Guide
Skin boils picture gallery sets the stage for a comprehensive visual guide to understanding these common skin conditions. This resource will provide clear images and descriptions of skin boils at various stages, helping you identify them accurately. We’ll explore different types, potential causes, and even treatment options. Learn how to distinguish skin boils from similar…
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Overview Understanding the Condition
Ehlers danlos syndrome overview – Ehlers-Danlos syndrome overview explores this complex group of connective tissue disorders. These conditions, often inherited, affect the body’s structure and function, impacting everything from skin elasticity to joint stability. This overview delves into the different types of EDS, their unique symptoms, and the challenges faced by those living with the…
How Myasthenia Gravis Is Diagnosed A Comprehensive Guide
How myasthenia gravis is diagnosed is a crucial process, often involving a multifaceted approach. This journey begins with recognizing the subtle and sometimes overlooked initial symptoms, progressing through neurological examinations, and culminating in a series of diagnostic tests. Understanding the various methods used in the diagnostic process can help patients and their families navigate this…
How Often Should I Wash My Face? Your Guide
How often should I wash my face? This question plagues many, but the answer isn’t one-size-fits-all. Your skin type, daily activities, and even the environment play a crucial role in determining the ideal washing frequency. This guide delves into the factors affecting your face-washing routine, offering personalized insights for healthy skin. We’ll explore various skin…
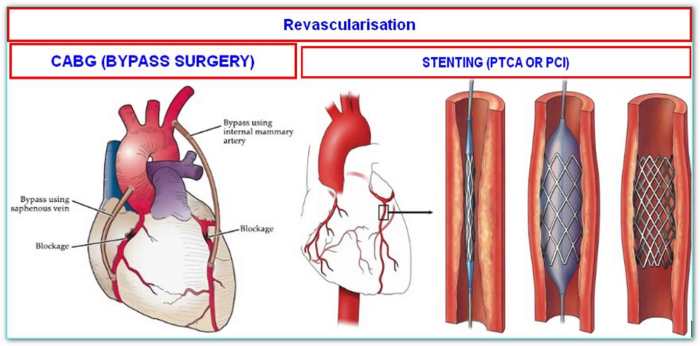
What is a Double Bypass Heart Surgery? A Comprehensive Guide
What is a double bypass heart surgery? This procedure, a significant step in cardiovascular care, aims to improve blood flow to the heart. It involves rerouting blood flow around blocked coronary arteries, often caused by atherosclerosis. Understanding the historical context, different types of bypasses, and the meticulous preparation and recovery process is crucial for patients…
Drool Rash vs Hand-Foot-Mouth A Deep Dive
Drool rash vs hand foot mouth – Drool rash vs hand-foot-mouth: Understanding these two viral infections is crucial for parents and caregivers. This post dives deep into the similarities and differences, exploring symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies for both conditions. Knowing the key distinctions can help you quickly identify which illness your child…