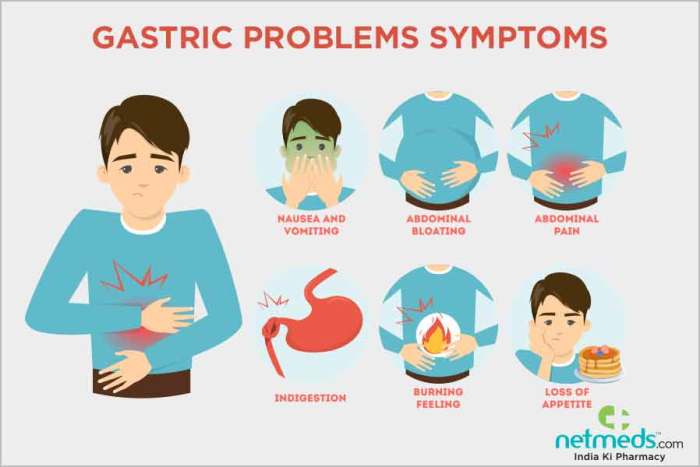
Tips for relieving intestinal gas through movement offers a practical approach to managing discomfort. This guide explores the connection between physical activity and digestive health, revealing how various movements can alleviate gas buildup. We’ll delve into specific exercises, posture, breathing techniques, and dietary considerations to create a personalized plan for gas relief. From gentle stretches…
Author: Jaiden Mayer
Can Probiotics Help Acid Reflux?
Can probiotics help with acid reflux? This question sparks curiosity and debate among those seeking natural remedies for this common digestive ailment. Acid reflux, characterized by the burning sensation in the chest, often arises from stomach acid backing up into the esophagus. While conventional treatments exist, many people explore alternative approaches, including probiotics. This exploration…
Natural Remedies to Restore pH Balance
Natural remedies to restore pH balance offer a holistic approach to wellness, focusing on the delicate equilibrium of your body’s internal environment. Understanding your body’s pH levels and the factors that contribute to imbalances is crucial for making informed choices. This exploration delves into dietary strategies, lifestyle practices, herbal remedies, and alternative therapies, providing insights…
Bipolar Disorder Hypersexuality Symptoms Explained
Symptoms of bipolar disorder hypersexuality can be a confusing and challenging aspect of the condition. It’s crucial to understand that this isn’t simply an increased libido, but a symptom often linked to the manic or mixed episodes of bipolar disorder. This in-depth look delves into the complexities of hypersexuality, exploring its triggers, impact on relationships,…
Foot Pain in Ball of Foot Causes, Symptoms, & Relief
Foot pain in ball of foot can be debilitating, affecting daily activities and overall well-being. This comprehensive guide delves into the common causes, symptoms, effective treatments, and preventative measures for this prevalent foot ailment. Understanding the root of the problem is crucial for finding lasting relief. We’ll explore various conditions like plantar fasciitis, metatarsalgia, and…
Worst Blood Pressure Drugs A Critical Look
Worst blood pressure drugs are a concern for many. This article dives deep into common complaints, potential risks, alternative treatments, patient experiences, and specific drug examples. We’ll examine the side effects, potential long-term consequences, and the importance of open communication with healthcare providers. Understanding the potential downsides of blood pressure medications is crucial for informed…
Birth Control While Breastfeeding Your Guide
Birth control while breastfeeding is a crucial aspect of postpartum planning. Hormonal changes during breastfeeding can impact your body, and choosing the right birth control method is essential. This comprehensive guide explores various options, considering their impact on milk supply, efficacy, and potential side effects. We’ll delve into hormonal and non-hormonal methods, the Lactational Amenorrhea…
How Long Does Viagra Last? A Detailed Look
How long does Viagra last? This crucial question affects many men’s experiences. Understanding the factors influencing Viagra’s duration is key to maximizing its effectiveness and managing expectations. From the typical timeframe to individual variations, this comprehensive guide delves into the science behind Viagra’s action and how it impacts different people. Viagra’s effectiveness isn’t a one-size-fits-all…
Stage 3 Breast Cancer Understanding the Journey
Stage 3 breast cancer presents a significant challenge, but understanding the specifics of this disease is crucial for navigating the treatment and recovery process. This comprehensive guide delves into the characteristics, diagnosis, treatment options, prognosis, and support systems available for those facing stage 3 breast cancer. The disease’s diverse subtypes and associated risk factors are…
Avocados Amazing Health Benefits
Health benefits of avocado are plentiful and impressive. This delicious fruit packs a powerful nutritional punch, offering a wide array of advantages for your overall well-being. From supporting heart health and healthy digestion to managing blood sugar and even promoting healthy skin, avocados are a versatile and valuable addition to any healthy diet. Let’s dive…