The four phases and tasks of grief sets the stage for this exploration of a deeply personal journey. It delves into the complexities of loss, offering a framework for understanding the emotional and behavioral responses that accompany grief. We’ll examine the unique experiences of individuals, discuss coping mechanisms, and explore the role of professional support…
Author: Jaiden Mayer
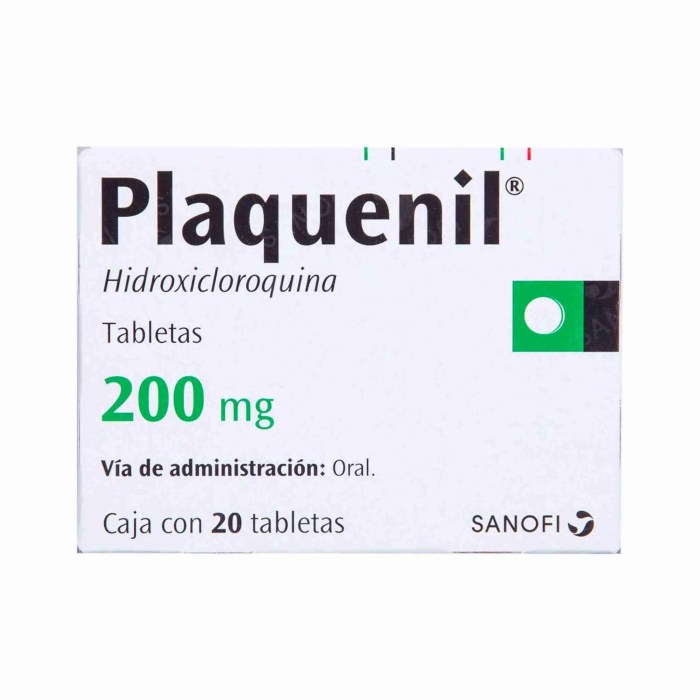
Plaquenil and Your Eyes A Deep Dive
Plaquenil and your eyes: This exploration delves into the potential eye-related side effects of this medication, examining the mechanisms behind them, risk factors, diagnosis, patient experiences, and comparisons with other treatments. Understanding the intricacies of this relationship is crucial for anyone considering or currently taking Plaquenil. We’ll cover everything from the specific symptoms you might…
Infant Asthma Symptoms A Comprehensive Guide
Symptoms of infant asthma can be subtle and easily confused with other common respiratory issues. Understanding the diverse presentations of these symptoms, both respiratory and non-respiratory, is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. This guide delves into the key characteristics, triggers, and diagnostic considerations related to infant asthma. From the initial introduction to the…
Quality Sleep While Taking Cymbalta
Quality sleep while taking Cymbalta can be a challenge for many, but understanding the potential effects and strategies to manage them can make a significant difference. This comprehensive guide explores the relationship between Cymbalta and sleep, from its mechanism of action to individual experiences, and offers practical advice for navigating sleep issues effectively. This exploration…
Which HIV Tests Are Most Accurate?
Which HIV tests are the most accurate? This question is crucial for ensuring accurate diagnoses and appropriate health management. Different HIV tests employ various methods, each with its own strengths and weaknesses regarding sensitivity, specificity, and speed. Understanding these differences is vital for making informed decisions about testing, and ultimately, for protecting your health. This…
Calf Strain Muscle Spasm of the Leg A Deep Dive
Calf strain muscle spasm of the leg is a common injury, often resulting from overuse or improper form during exercise. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of this condition, from its anatomical underpinnings to effective treatment and preventative measures. We’ll delve into the specific muscles involved, the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and recovery strategies, offering insights…
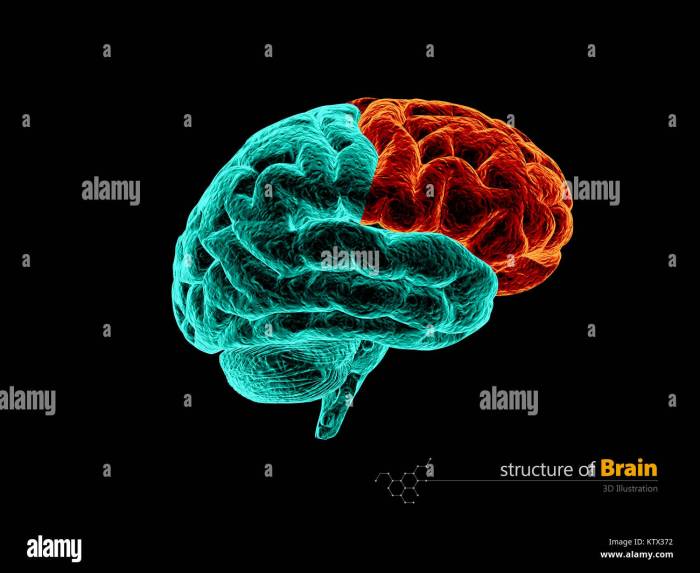
The Brains Frontal Lobe A Deep Dive
The brains frontal lobe – The brain’s frontal lobe sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This crucial part of the brain, located at the front of the cerebral cortex, plays a pivotal role in everything…
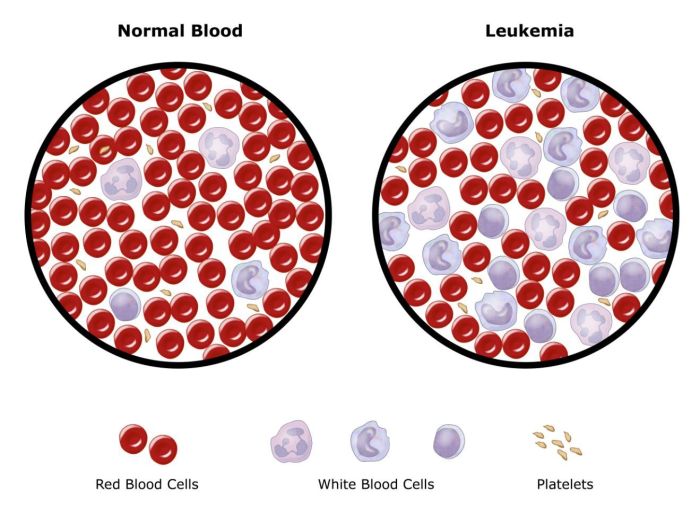
Major Differences Between Leukemia and Lymphoma
Major differences between leukemia and lymphoma are crucial for understanding these blood cancers. While both are serious, they originate from different cells and have distinct characteristics in their symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. This exploration delves into the key distinctions between these often-confused diseases. Leukemia and lymphoma, though both categorized as blood cancers, represent vastly…
Metastatic Breast Cancer Support A Comprehensive Guide
Areas of support for someone with metastatic breast cancer are crucial for navigating the complexities of this journey. This guide delves into various support systems, from the vital emotional and practical resources available, to navigating the healthcare system and finding community support. We’ll explore everything from building strong relationships to understanding financial aid options and…
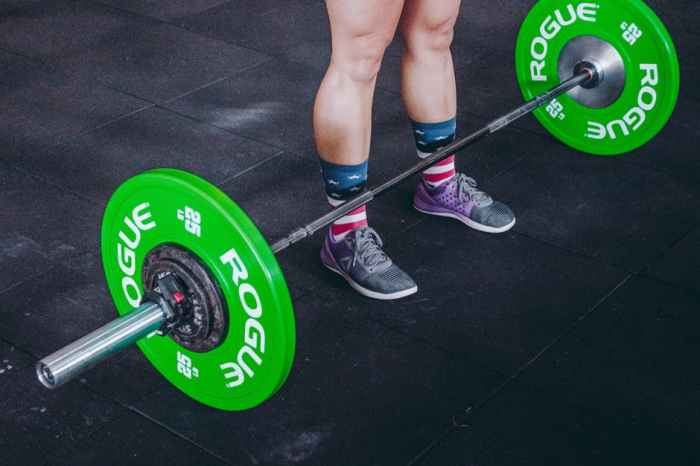
How to Build Strength Your Complete Guide
How to build strength? This comprehensive guide dives deep into the multifaceted world of strength training, exploring everything from physical muscle development to the crucial role of mental fortitude. We’ll cover various training methods, nutrition strategies, and essential safety precautions to help you achieve your strength goals, whether you’re a seasoned athlete or just starting…