Post SSRI erectile dysfunction is a complex issue affecting many individuals taking selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). This in-depth exploration delves into the potential link between SSRIs and sexual dysfunction, examining the various mechanisms involved, the symptoms experienced, and available treatment options. We’ll also discuss underlying factors and preventative strategies. Understanding the potential for SSRIs…
Author: Jaiden Mayer
Foods to Avoid with Macular Degeneration A Guide
Foods to avoid with macular degeneration are crucial for managing this condition. This guide dives into the specific dietary choices that can either support or hinder your eye health. Understanding which foods contribute to macular degeneration’s progression and which ones offer protective antioxidants is key to preserving vision. Macular degeneration, a common age-related eye disease,…
How Should I Eat After a Colostomy?
How should I eat after a colostomy? This is a crucial question for anyone facing this life change. Adjusting your diet after a colostomy is a journey of discovery, learning what foods work best for your unique body and colostomy. This guide dives into the dietary considerations, helping you understand the necessary changes and strategies…
Levemir Discontinued? How to Switch Insulin
Levemir discontinued how to switch insulin? This comprehensive guide dives into the process of transitioning from Levemir to a different insulin regimen. We’ll explore why your doctor might choose to discontinue Levemir, the steps involved in the switch, and important considerations for specific patient groups. Understanding the nuances of insulin management is crucial, and this…
Alcohol & Arthritis Drugs Is It Forbidden?
Is alcohol forbidden when taking arthritis drugs? This crucial question impacts many people living with arthritis, demanding careful consideration of potential interactions. Different arthritis medications interact with alcohol in various ways, and understanding these interactions is vital for safe and effective treatment. This post will delve into the potential risks and benefits, providing valuable insights…
Coping When Loved One Doesnt Recognize You
Coping when loved one doesnt recognize you – Coping when a loved one doesn’t recognize you is a deeply challenging experience, filled with a spectrum of emotions and complex situations. This journey explores the emotional toll of such a situation, from the initial shock and confusion to the potential long-term impact on the relationship. We’ll…
Adenosis Enlarged Breast Lobules A Comprehensive Guide
Adenosis enlarged breast lobules is a condition characterized by the abnormal growth of the milk-producing glands within the breasts. Understanding the intricacies of this condition, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and management, is crucial for both patients and healthcare professionals. This guide delves into the various aspects of adenosis enlarged breast lobules, providing a clear…
Can GERD Cause Heart Palpitations?
Can GERD cause heart palpitations? This is a question that often arises for those experiencing both acid reflux and unusual heart sensations. Understanding the potential link between these two seemingly disparate conditions is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management. This exploration dives deep into the possible connections, symptoms, and considerations, helping readers navigate this…
Conversation Issues Discussing Psoriasis A Deep Dive
Conversation issues discussing psoriasis are complex, encompassing a wide range of challenges faced by those living with the condition. This exploration delves into the nuances of communication, from understanding the emotional toll to navigating difficult conversations in various settings, including family, friendships, and the workplace. We’ll also examine the crucial role of support communities and…
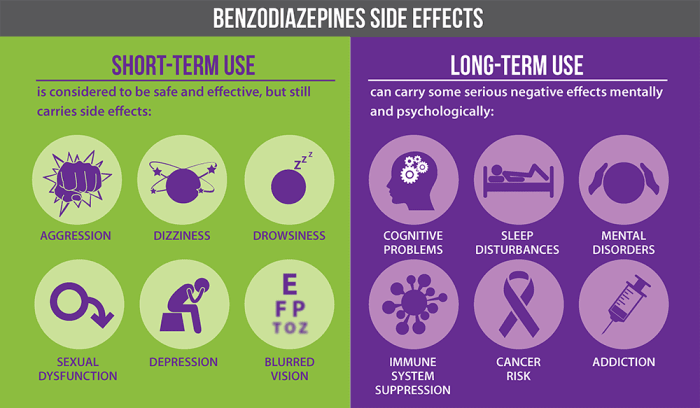
Benzodiazepines Uses, Types, and Risks
Uses types and risks of benzodiazepines – Benzodiazepines: Uses, Types, and Risks sets the stage for a detailed exploration of these medications. This in-depth look will cover everything from their chemical makeup and mechanism of action to their various applications, potential dangers, and long-term considerations. We’ll analyze different types, examining their potency, duration, and common…