Benefits of ganoderma coffee are gaining popularity as people seek natural ways to enhance their well-being. This exploration delves into the potential health advantages of this unique brew, examining its ingredients, preparation, and the science behind its possible effects. We’ll uncover the historical context, potential benefits, potential drawbacks, and more, offering a comprehensive look at…
Author: Herman Swift
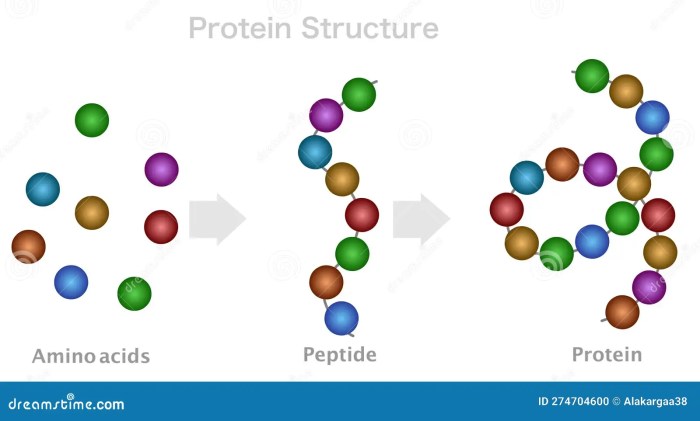
What is a Peptide A Deep Dive
What is a peptide? This exploration delves into the fascinating world of peptides, those short chains of amino acids that play crucial roles in various biological processes. From their fundamental structure to their diverse functions in nature and medicine, we’ll uncover the secrets behind these remarkable molecules. Prepare to embark on a journey into the…
Natural Remedies and Supplements for Gallbladder Issues
Natural remedies and supplements for gallbladder issues offer a range of potential solutions, from dietary changes to herbal remedies. Understanding how these approaches work and their potential benefits, along with potential risks, is key to making informed choices. This exploration delves into various natural strategies for gallbladder support, emphasizing the importance of consulting with a…
Damiana What Should I Know About It?
Damiana what should i know about it – Damiana, what should I know about it? This comprehensive guide dives into the fascinating world of Damiana, exploring its botanical origins, traditional uses, modern research, potential benefits and risks, safety considerations, and even how to grow it yourself. We’ll uncover its history, medicinal applications across cultures, and…
Decoding Blood Ketone Test Results
How to read blood ketone test results is crucial for understanding your body’s metabolic state. This guide breaks down everything you need to know, from interpreting different ranges to understanding the implications of your specific results. We’ll explore various scenarios, including those for people with diabetes or following a ketogenic diet, and provide actionable steps…
Too Much Vitamin D A Deep Dive
Too much vitamin D, while crucial for bone health, can be detrimental if not managed properly. This comprehensive guide delves into the dangers of excessive vitamin D intake, exploring the defining factors, potential sources, and the serious implications for various demographics. We’ll uncover the symptoms, risk factors, and crucial strategies for prevention and management. Understanding…
How Often Can You Donate Blood? Your Guide
How often can you donate blood? This comprehensive guide dives into the fascinating world of blood donation frequency, exploring the recommended intervals, eligibility criteria, and the vital role blood donations play in public health. We’ll cover everything from the science behind blood donation to the practical steps involved in the process, making sure you’re well-informed…
Amycretin Novo Nordisk Obesity Drug A Deep Dive
Amycretin Novo Nordisk obesity drug is a new treatment for weight management, promising significant results. This article explores its mechanism of action, clinical trial data, potential side effects, and the broader implications for patients and the obesity treatment landscape. Understanding the intricacies of this novel approach to weight loss is key to evaluating its efficacy…
Krill vs Fish Oil A Deep Dive
Krill vs fish oil: This in-depth comparison explores the nutritional differences and potential health benefits of these popular omega-3 supplements. Krill oil, derived from tiny crustaceans, boasts unique properties, while fish oil, a familiar choice, offers a wealth of omega-3 fatty acids. Understanding the nuances of each can empower informed dietary decisions. Both krill and…
Cialis vs Viagra Effectiveness, Dosage, and Safety
Cialis vs viagra effectiveness dosage and safety – Cialis vs Viagra: effectiveness, dosage, and safety is a crucial consideration for anyone exploring treatment options for erectile dysfunction (ED). This in-depth look examines the similarities and differences between these popular PDE5 inhibitors, covering their effectiveness, recommended dosages, potential side effects, and patient considerations. Understanding the nuances…