Autoimmunity neuroinflammation in fibromyalgia is a fascinating and complex area of research. This condition, characterized by widespread pain and fatigue, is increasingly understood to involve interactions between the immune system and the nervous system. We’ll delve into the potential mechanisms by which these processes intertwine, exploring the suspected roles of autoimmunity and neuroinflammation in the…
Author: Herman Swift
Overview of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia A Comprehensive Look
Overview of chronic myeloid leukemia is a complex blood cancer, and understanding its intricacies is crucial for those affected and those seeking to learn more. This introduction will explore the various facets of CML, from its defining characteristics and underlying pathophysiology to the available treatment strategies and future research directions. Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is…
Complete Blood Count CBC Analyzer A Deep Dive
Complete blood count CBC analyzer technology has revolutionized diagnostics, providing crucial insights into patient health. This comprehensive guide delves into the inner workings of these sophisticated machines, exploring everything from their historical development to the latest advancements. We’ll uncover the various types, components, operational procedures, data interpretation, and even the safety protocols involved. Get ready…
Facts About Fluoride Toothpaste A Comprehensive Guide
Facts about fluoride toothpaste are essential for understanding its role in oral health. This guide delves into the history, composition, benefits, and potential risks associated with fluoride toothpaste. We’ll explore different types, usage recommendations, and compare fluoride toothpastes with alternatives. From its historical context in dentistry to the chemical composition of common varieties, this in-depth…
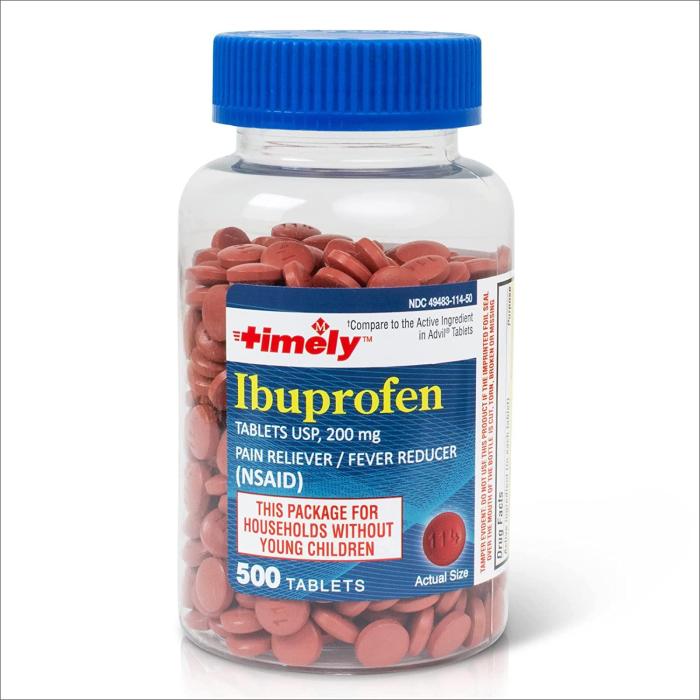
Ibuprofen Dosage How Much Is Safe?
Ibuprofen dosage how much you can safely take – Ibuprofen dosage: how much you can safely take is a crucial aspect of responsible pain and fever management. Understanding the appropriate dosage for both adults and children, along with potential side effects and interactions, is essential. This comprehensive guide delves into the various facets of ibuprofen…
How Long Does Constipation Last? A Deep Dive
How long does constipation last? This isn’t just an annoying question; understanding the duration is crucial for effective management. From mild discomfort to severe distress, the length of time constipation lingers varies significantly. This exploration delves into the factors influencing duration, from dietary changes to underlying health issues, providing insights into when to seek professional…
When Back Pain Is Serious Understanding the Signs
When back pain is serious, it’s crucial to understand the potential indicators and know when to seek immediate medical attention. This comprehensive guide delves into the various symptoms, underlying conditions, diagnostic procedures, and treatment options associated with serious back pain. We’ll explore the nuances between acute and chronic pain, red flag symptoms, and the importance…
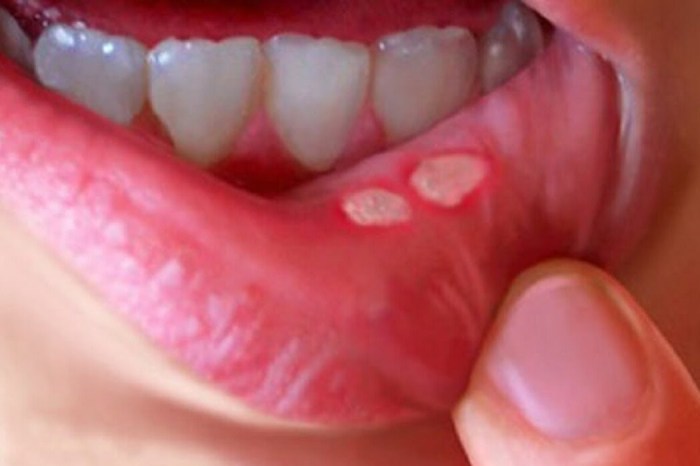
Canker Sore on Tongue A Comprehensive Guide
Canker sore on tongue, those pesky little ulcers that pop up in the mouth, can be incredibly frustrating. This guide dives deep into understanding these painful sores, from their causes and symptoms to effective home remedies and when to seek professional help. We’ll explore everything you need to know about identifying, treating, and preventing canker…
Is Blood Pressure Higher in the Morning? Exploring the Why
Is blood pressure higher in the morning? Yes, it often is, and understanding why this happens is crucial for managing your overall health. Our bodies have a natural rhythm, or circadian rhythm, that influences many functions, including blood pressure. This morning peak in blood pressure isn’t necessarily a cause for alarm, but knowing the factors…
Right Handed Left Handed Stroke Differences
Right handed left handed stroke different reveals fascinating variations in how we write. From the subtle grip to the trajectory of our strokes, there’s a world of difference between right and left-handed individuals. This exploration dives into the characteristics of each hand’s writing style, the impact on writing tools, the developmental stages of learning, and…