Traditional Chinese Medicine overview explores the rich history and diverse practices of this ancient healing system. From its roots in centuries-old philosophies to its modern applications, TCM offers a unique perspective on health and well-being. This exploration delves into the fundamental principles, key components of practice, treatment modalities, and its relevance in addressing modern health…
Author: Deontae Botsford
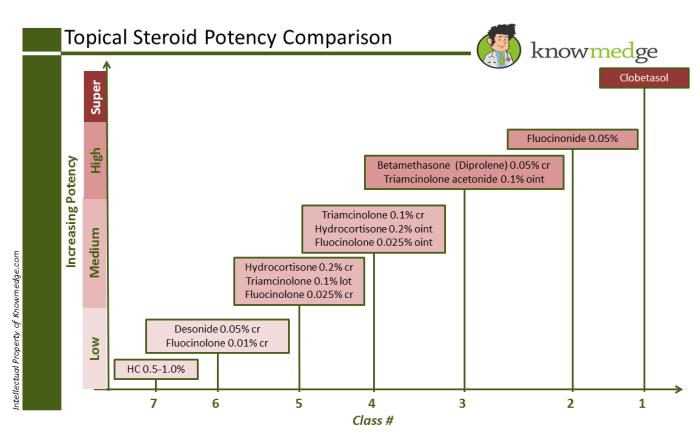
Steroids Topical Steroid Strengths A Deep Dive
Steroids topical steroid strengths are crucial for treating various skin conditions. This guide delves into the different potencies, their applications, and potential side effects. Understanding the strengths and appropriate usage is vital for effective treatment and minimizing adverse reactions. We’ll explore the diverse range of skin conditions treatable with topical steroids, examining the factors determining…
Nkem Osians Uterine Fibroid Story A Personal Account
Nkem osian uterine fibroid story – Nkem Osian’s uterine fibroid story is a powerful account of navigating a health challenge with resilience and grace. This journey delves into the personal experiences, medical treatments, and societal factors surrounding uterine fibroids. From understanding the condition itself to exploring the emotional and practical impacts, this narrative offers a…
Gallbladder Surgery Long-Term Care Your Guide
Gallbladder surgery long term care – Gallbladder surgery long-term care is crucial for a smooth recovery and overall well-being. This guide delves into the essential aspects of post-operative life, covering everything from the recovery timeline and dietary adjustments to managing potential complications and the importance of follow-up care. Understanding these factors empowers you to make…
Top Fish Choices for Protein Boost
Top fish choices to boost your protein intake are a fantastic way to nourish your body with essential nutrients. From the delicate flavors of salmon to the firm texture of tuna, a variety of fish offer an excellent source of high-quality protein, alongside vital vitamins and minerals. This guide explores the best fish options, delves…
How to Change Your Eye Color A Deep Dive
How to change your eye color? This isn’t about magic; it’s a journey into the fascinating world of eye color alteration. We’ll explore the myths, the realities, the science behind our irises, and the surprising ways people have tried to change their eye color throughout history. From temporary tricks to more permanent procedures, we’ll dissect…
Hyperpathia, Hyperalgesia, Hypersensitivity A Deep Dive
Hyperpathia hyperalgesia and hypersensitivity – Hyperpathia, hyperalgesia, and hypersensitivity: these terms describe heightened pain experiences, but what exactly do they mean? This exploration delves into the intricacies of these conditions, from defining each distinct pain response to understanding the underlying mechanisms and how they affect daily life. We’ll uncover the various causes, diagnostic methods, treatment…
Silicone Hydrogel Contact Lenses A Deep Dive
Silicone hydrogel contact lenses have revolutionized vision correction, offering unparalleled comfort and enhanced eye health. These lenses, meticulously crafted from a blend of silicone and hydrogel, boast superior oxygen permeability compared to traditional materials. This allows for extended wear and reduces the risk of dry eyes, a common concern with other types of contact lenses….
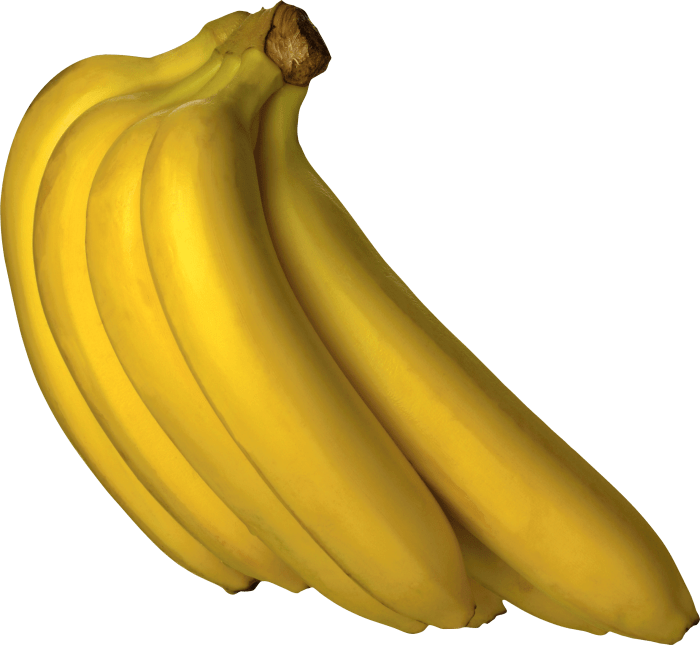
Are Bananas Good for You? A Deep Dive
Are bananas good for you? This comprehensive exploration dives into the nutritional value, health benefits, culinary uses, potential risks, and even the cultural significance of this beloved fruit. We’ll uncover the surprising details behind this popular snack, from its potassium powerhouse potential to its role in various diets. From a detailed breakdown of vitamins and…
What is Crohns Colitis? A Deep Dive
What is crohns colitis – What is Crohn’s Colitis? This chronic inflammatory condition affects the digestive tract, causing a range of symptoms and impacting daily life. Understanding the nuances of this complex disease, from its causes and stages to potential complications and treatment options, is crucial for those affected and those seeking to learn more….