Ella vs Plan B: This in-depth comparison explores the key differences between EllaOne and Plan B, two emergency contraceptive options. We’ll delve into their active ingredients, potential side effects, effectiveness, cost, and accessibility. Understanding these factors can help individuals make informed decisions about their reproductive health. From active ingredients and dosages to potential side effects…
Author: Deontae Botsford
Fish Oil Supplements AFib Risk A Deep Dive
Fish oil supplements AFib risk is a complex issue, with ongoing research attempting to unravel the potential connections between these dietary supplements and the development of Atrial Fibrillation (AFib). This blog post delves into the science behind fish oil’s purported cardiovascular benefits and examines the existing evidence linking fish oil intake to AFib risk. We’ll…
Back Pain A Lung Cancer Symptom
Back pain as a symptom of lung cancer is a complex and often overlooked possibility. While back pain is frequently associated with other conditions, its unusual manifestation in relation to lung cancer warrants careful consideration. This exploration delves into the potential link, highlighting the various ways back pain can manifest, its location, characteristics, and the…
Chipotle Food Allergy Information A Guide
Chipotle food allergy information is crucial for ensuring a safe dining experience for everyone. This guide dives deep into the specifics of common food allergies, Chipotle’s ingredients, cross-contamination risks, and how to communicate effectively about allergies within the restaurant. We’ll explore the legal requirements and best practices, empowering both Chipotle staff and customers with the…
How Graft-Versus-Host Disease GvHD Is Diagnosed
How graft versus host disease GvHD is diagnosed is a crucial aspect of patient care. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of identifying GvHD, from understanding its underlying mechanisms to employing various diagnostic tools. We’ll explore the different types of GvHD, their clinical manifestations, and the essential factors to consider when evaluating a patient…
When Should I Take the Pill? A Comprehensive Guide
When should I take the pill? This crucial question affects everything from medication effectiveness to overall well-being. Understanding the nuances of different pill types, their absorption rates, and potential interactions is key to optimizing your health. This guide provides a detailed exploration of various pill types, schedules, and factors influencing optimal timing, offering practical advice…
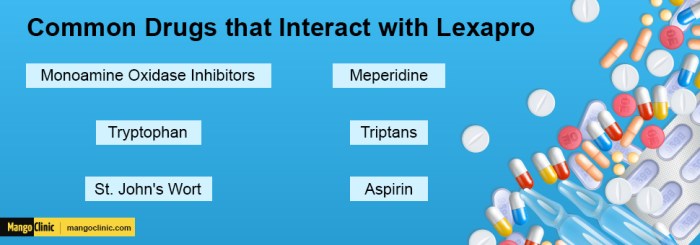
Prozac Fluoxetine vs Lexapro Escitalopram A Deep Dive
Prozac fluoxetine vs lexapro escitalopram: A comparison of these two popular antidepressants, both Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs), is crucial for individuals seeking effective treatment. This in-depth look examines their mechanisms of action, common side effects, dosage ranges, and potential interactions. Understanding the nuances between these drugs empowers informed decision-making with a healthcare professional. This…
Hyvelle Fergusons Type 2 Diabetes Journey
Hyvelle ferguson my journey with type 2 diabetes – Hyvelle Ferguson’s journey with type 2 diabetes offers a compelling personal account of navigating a chronic condition. This in-depth exploration dives into the challenges and triumphs of managing type 2 diabetes, sharing insights into her experiences and strategies. From understanding the fundamental mechanisms of type 2…
Pool/Hot Tub Electrocution Risk How Likely?
How likely is it to get electrocuted in a pool or hot tub? This exploration delves into the factors contributing to electrocution risk around these water features. From electrical system safety to user behavior, we’ll examine the potential hazards and provide crucial safety measures. Understanding the difference between direct and indirect contact with electricity, along…
Types of Weight Loss Surgery A Comprehensive Guide
Types of weight loss surgery encompass a spectrum of procedures, each with its own unique mechanisms, benefits, and drawbacks. Understanding these different approaches is crucial for individuals considering this option. This guide delves into the various surgical interventions available, from restrictive to malabsorptive, and combined techniques. We’ll explore the historical context, surgical mechanisms, potential complications,…