How to use crutches sets the stage for this in-depth guide, covering everything from understanding different crutch types to mastering safe techniques for various terrains and activities. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to navigate daily life while using crutches safely and effectively. Whether you’re a recent user or looking to…
Author: Deontae Botsford
How to Plan a Funeral or Memorial Service A Comprehensive Guide
How to plan a funeral or memorial service is a crucial guide for navigating the sensitive process of honoring a loved one. This comprehensive guide will walk you through every step, from understanding individual needs and preferences to managing finances and arranging the reception. Whether you’re facing a traditional ceremony or a modern celebration of…
Type 2 Diabetes in Black and Brown People A Deep Dive
Type 2 diabetes in black and brown people is a critical health issue demanding attention. This exploration delves into the significant prevalence rates and the unique risk factors impacting these communities. We’ll examine the challenges in diagnosis, the need for culturally appropriate management strategies, and the role of social determinants of health in shaping these…
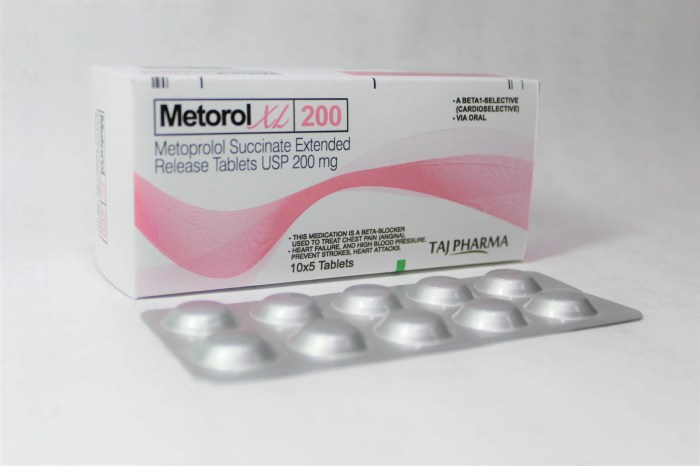
How Long Does Metoprolol Take to Work?
How long does it take for metoprolol to work? This crucial question often arises for patients prescribed this beta-blocker. Understanding the factors influencing its onset, from dosage to individual physiology, is key to managing expectations and ensuring effective treatment. This exploration delves into the intricacies of metoprolol’s action, examining the timeframes involved in achieving its…
Hyaluronic Acid for Hair A Deep Dive
Hyaluronic acid for hair is a fascinating topic. This exploration delves into the science behind its potential benefits, examining different types and their applications in hair care. We’ll uncover the historical use of hyaluronic acid in beauty, debunk common myths, and discuss the mechanisms through which it might affect hair follicles. From hydration and elasticity…
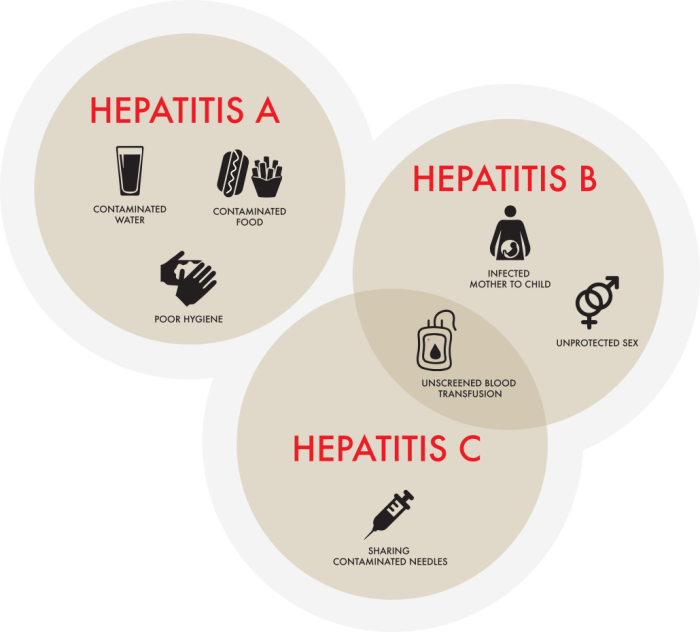
Which Hepatitis is the Worst? A Deep Dive
Which hepatitis is the worst? This question often arises, but there’s no single answer. The severity of hepatitis, a liver inflammation, varies significantly depending on the type (A, B, C, D, E) and individual factors. Understanding the different types, their transmission methods, and the potential long-term consequences is crucial for informed discussion. This exploration delves…
How to Reverse Atrial Fibrillation Naturally A Guide
How to reverse atrial fibrillation naturally is a crucial question for many seeking alternative or complementary approaches to managing this condition. This guide delves into potential lifestyle modifications, dietary recommendations, herbal remedies, nutritional considerations, and mind-body practices that may help. We’ll explore various strategies, but remember that natural remedies are not a substitute for professional…
Donating Hair for Cancer Patients A Compassionate Act
Donating hair for people with cancer is a profoundly compassionate act that touches the lives of countless individuals. It’s a simple gesture that can offer remarkable emotional support and practical benefits to those undergoing the challenging journey of cancer treatment. This act of kindness involves a meticulous process, from understanding the different types of hair…
Baby Rash on Face A Comprehensive Guide
Baby rash on face can be a common and sometimes concerning issue for parents. This guide delves into the various types of rashes, their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventative measures. We’ll explore everything from heat rash to allergic reactions, providing a comprehensive understanding to help you identify and manage these skin conditions effectively….
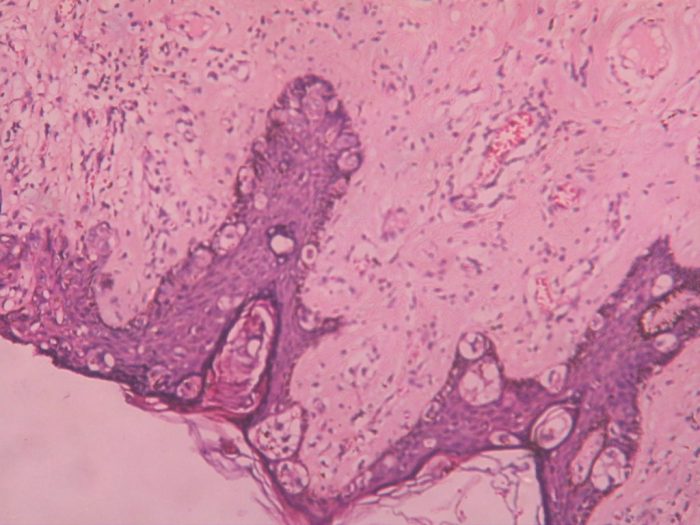
Pagets Disease of the Breast A Comprehensive Guide
Pagets disease of the breast – Paget’s disease of the breast is a rare skin condition that often presents as a rash or eczema-like lesion on the nipple or areola. Understanding this condition, from its characteristics to treatment options, is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of…