How long does it take for HIV to progress to AIDS? This complex question delves into the intricacies of HIV infection, from initial exposure to the development of AIDS. Understanding the stages, factors influencing progression, and the crucial role of treatment is key to comprehending this disease. This exploration will cover the science behind HIV,…
Author: Ceasar Ritchie
Parasitic CNS Infections A Deep Dive
Parasitic infections of the central nervous system are a significant global health concern. These infections, often insidious and diverse in their manifestations, can affect individuals worldwide. Understanding the various transmission routes, types of parasites involved, and the resulting pathologies is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. This comprehensive exploration will delve into the complexities of…
What are the Physical Effects of Sleep Deprivation?
What are the physical effects of sleep deprivation? This exploration delves into the immediate and long-term consequences of insufficient sleep, from reduced alertness to serious health risks. We’ll examine how sleep loss impacts various organ systems, physical performance, and even dietary habits. Understanding these effects is crucial for prioritizing sleep and maintaining overall well-being. Sleep…
Free HIV Testing Your Questions Answered
Ask an expert when and how can I get free HIV testing? This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about accessing free HIV testing services, from understanding the different types of tests to finding local resources and preparing for the process. We’ll cover everything from eligibility criteria to the importance of confidentiality and…
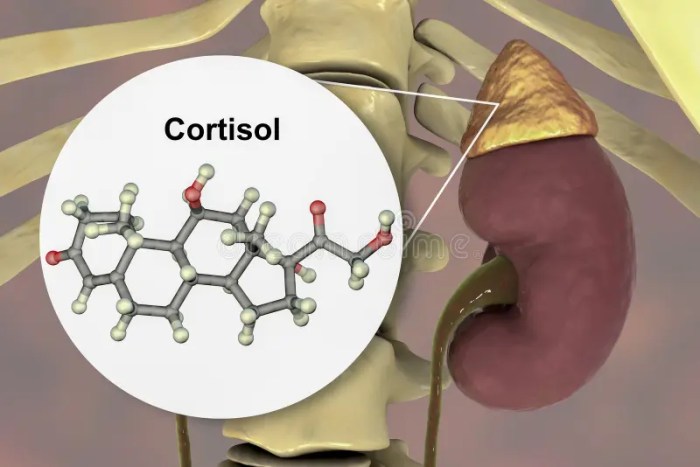
Cortisol Test What to Expect A Comprehensive Guide
Cortisol test what to expect? This guide provides a thorough overview of the process, from understanding the purpose and types of tests to interpreting results and potential outcomes. We’ll explore everything you need to know to prepare for this important medical procedure and feel more confident throughout the experience. This comprehensive guide covers various aspects…
Type 2 Diabetes Meal Planning Your Guide
Type 2 diabetes meal planning is crucial for managing blood sugar levels and overall health. This comprehensive guide delves into the essential principles, practical strategies, and resources to create a personalized meal plan that fits your needs and lifestyle. We’ll explore everything from macronutrient distribution to carbohydrate counting, healthy food choices, and even meal planning…
New Hair, New Look After Chemo A Guide
New hair new look after chemo – New hair, new look after chemo sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with personal stories. This journey delves into the emotional and practical aspects of embracing a new hairstyle during and after chemotherapy,…
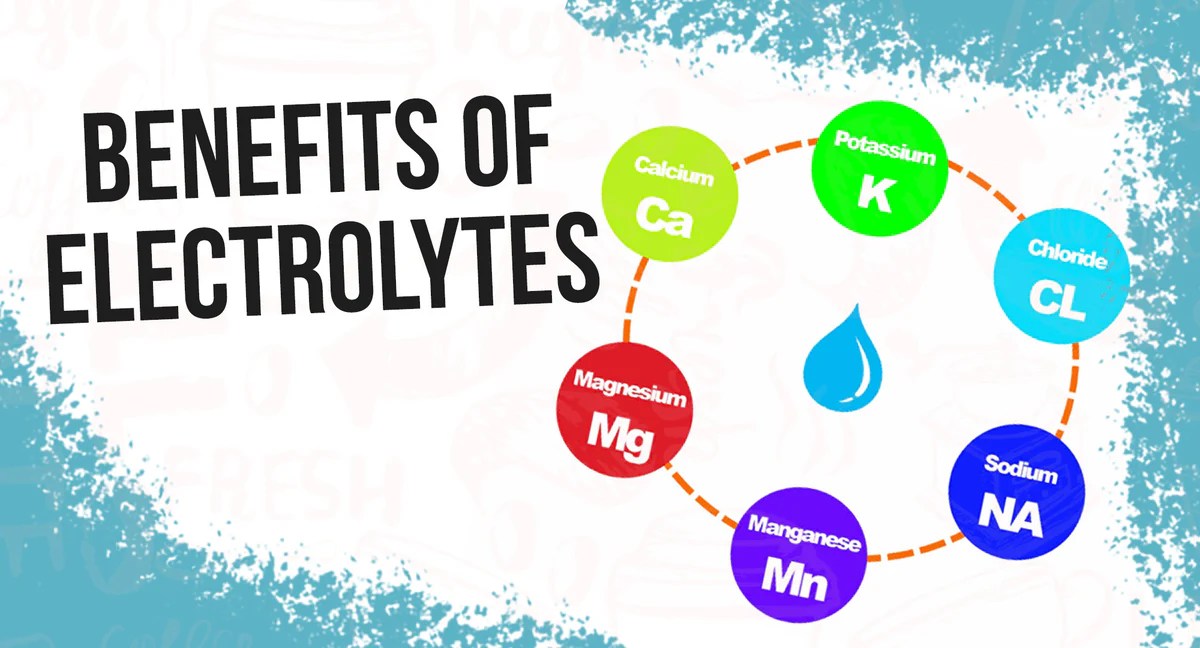
What Happens When Your Body Is Low on Electrolytes
What happens when your body is low on electrolytes sets the stage for a fascinating exploration into the vital role these minerals play in our well-being. Electrolytes, essential minerals like sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium, are crucial for a multitude of bodily functions. From nerve impulses to muscle contractions, and from hydration to blood pressure…
The Difference Between Overweight and Obesity A Deep Dive
The difference between overweight and obesity is often misunderstood. This blog post delves into the nuances of these conditions, exploring definitions, measurement methods, and the crucial distinction between them. We’ll uncover the factors contributing to their development, examine their health implications, and discuss effective prevention and management strategies. From genetics to lifestyle choices, we’ll unpack…
Rosemary Oil Hair Growth A Comprehensive Guide
Rosemary oil hair growth is a topic gaining traction, and for good reason. From ancient remedies to modern scientific explorations, the potential of this fragrant oil for promoting healthy hair has been widely discussed. This guide delves into the science behind rosemary oil’s purported benefits, exploring its mechanisms of action, research findings, and practical application….