High protein low fat foods are gaining popularity as a healthy eating approach. This guide delves into the world of these nutritious choices, exploring their history, benefits, and practical applications. We’ll cover everything from specific food examples and nutritional profiles to meal planning and potential health implications. This comprehensive exploration examines various aspects of high…
Author: Ceasar Ritchie
Reasons You Are Not Losing Weight Unveiling the Truth
Reasons you are not losing weight? It’s a common struggle, and often the answers lie beyond the obvious. This exploration delves into the multifaceted reasons behind weight loss plateaus, examining dietary choices, physical activity levels, lifestyle habits, potential underlying health conditions, and the crucial role of mindset. We’ll uncover the hidden factors that might be…
Treating Psoriasis on Hands and Feet A Comprehensive Guide
Treating psoriasis on your hands and feet can be a challenging journey, but understanding the condition and exploring various treatment options is crucial for managing symptoms effectively. This guide delves into the intricacies of hand and foot psoriasis, providing a comprehensive overview of its causes, symptoms, and a range of treatment approaches, from topical medications…
What is Levator Ani Syndrome? A Deep Dive
What is levator ani syndrome? This condition affects the pelvic floor muscles, specifically the levator ani, causing a range of symptoms and impacting daily life. Understanding the anatomy, potential causes, and available treatment options is key to managing this often-overlooked health issue. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of levator ani syndrome, equipping you…
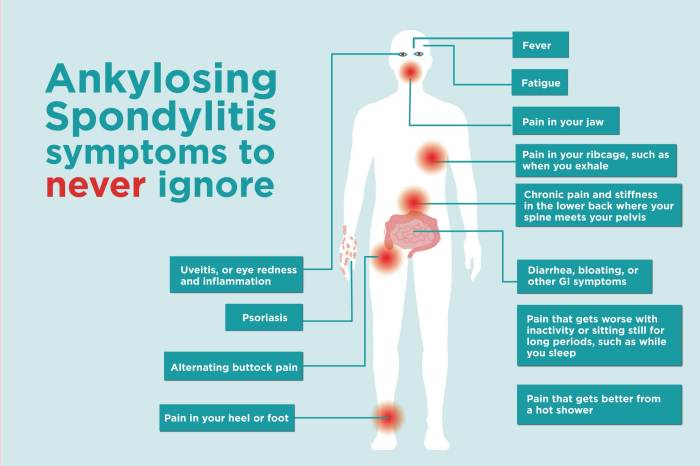
Ankylosing Spondylitis and Teeth Problems A Deep Dive
Ankylosing spondylitis and teeth problems are intricately linked, creating a complex interplay between spinal health and oral well-being. This exploration delves into the specifics of this connection, examining the common oral health concerns associated with AS, the underlying mechanisms, and effective management strategies. This comprehensive guide will cover various aspects of oral health in individuals…
Physical Therapy After Fracture Hardware Removal Your Recovery Guide
Physical therapy after fracture hardware removal is crucial for a successful recovery. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed overview of the process, from initial assessments to returning to daily activities. We’ll explore the different types of fractures requiring hardware removal, common exercises, pain management strategies, and the importance of gradual mobility restoration. We’ll also discuss…
What are Common Flu Shot Reactions? A Guide
What are common flu shot reactions? This guide dives into the possible side effects of getting a flu shot, from mild discomfort to more serious concerns. We’ll explore the various types of reactions, how long they typically last, and when you should seek medical attention. Understanding these reactions can help you feel more prepared and…
Flying with Heart Disease Essential Guidelines
Guidelines for flying with heart disease provide crucial information for safe and comfortable air travel. This comprehensive guide covers everything from pre-flight preparation to post-flight considerations, ensuring passengers with heart conditions can travel with confidence and peace of mind. From meticulously planning your medications and dietary needs to understanding in-flight procedures and choosing the right…
How to Check Blood Pressure at Home A Complete Guide
How to check blood pressure at home sets the stage for understanding your vital signs. Regular monitoring is crucial for both personal health and proactive communication with your doctor. This guide will walk you through the process, from choosing the right monitor to interpreting your results and maintaining a blood pressure log. We’ll cover everything…
Ringing in Ears Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Ringing in ears symptoms causes and treatment is a complex issue affecting many people. This comprehensive guide explores the various aspects of tinnitus, from understanding its different types and symptoms to exploring potential causes, diagnosis methods, and a range of treatment options. We’ll delve into lifestyle modifications and management strategies, including coping mechanisms and stress…