The health benefits of bifobacterium – The health benefits of bifidobacterium are increasingly recognized for their positive impact on human well-being. This comprehensive exploration delves into the fascinating world of these beneficial bacteria, examining their role in digestive health, immune support, and potential impact on overall wellness. We’ll uncover how bifidobacteria work, their various species…
Author: Ceasar Ritchie
Asymptomatic Definition Importance and Controversy
Asymptomatic definition importance and controversy is a complex and crucial aspect of public health. Understanding how we define the absence of symptoms is essential for effective disease prevention and control strategies. This multifaceted issue involves diverse perspectives, ranging from medical definitions to public health implications, ethical considerations, and practical challenges in identification. Different medical and…
Things to Stop for a Longer Life
Things to stop if you want to live longer: This post delves into crucial lifestyle choices that can significantly impact your lifespan. We’ll explore the negative effects of unhealthy habits and offer actionable strategies to cultivate healthier practices. From diet and exercise to stress management and sleep hygiene, we’ll cover a comprehensive approach to a…
Sore Throat and Cough Understanding Causes and Relief
Sore throat and cough – a common ailment affecting people of all ages. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of these symptoms, exploring everything from their various characteristics to potential causes and effective treatment options. We’ll examine how symptoms differ between adults and children, uncover common triggers, and compare them to similar conditions like…
Lymph Node Positive Breast Cancer A Comprehensive Guide
Lymph node positive breast cancer presents a significant challenge, but understanding the complexities of this condition is crucial for navigating the journey ahead. This guide delves into the specifics of lymph node involvement, exploring its implications for prognosis, treatment, and ultimately, the patient’s well-being. We’ll uncover the different stages of lymph node involvement, compare it…
Can Pregnant Women Eat Shrimp? A Deep Dive
Can pregnant women eat shrimp? This crucial question confronts expectant mothers, navigating a world of nutritional needs and potential risks. Shrimp, a delicious and versatile seafood, offers a wealth of nutrients, but concerns about food safety and potential contaminants like mercury must be considered. This exploration delves into the nutritional value of shrimp, the potential…
Can I Keep Working with Fibromyalgia and CFS?
Can I keep working with fibromyalgia and CFS? This question is crucial for many, as these conditions can significantly impact daily life and work performance. This guide explores the complexities of maintaining employment while living with fibromyalgia (FM) and chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), providing insights into understanding these conditions, exploring work options, managing symptoms, and…
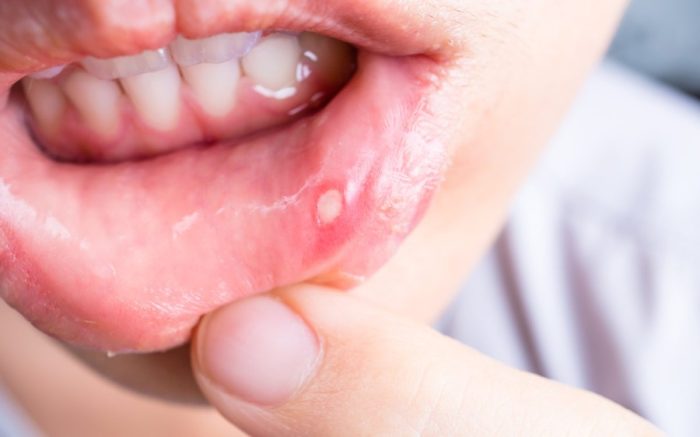
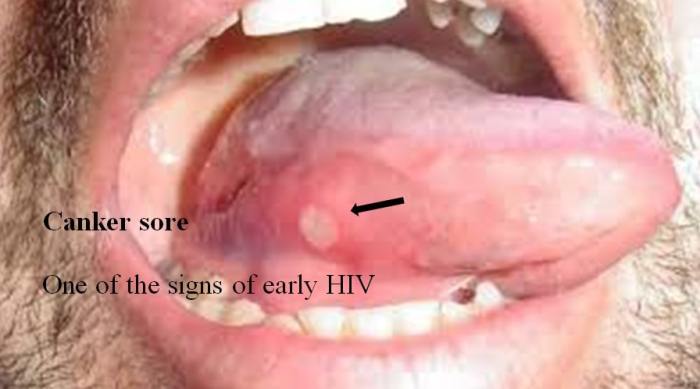
HIV Mouth Sores Pictures Visual Guide
HIV mouth sores pictures offer a crucial visual aid for understanding the oral manifestations of HIV. Identifying these sores early is vital for proper diagnosis and treatment. This guide will visually illustrate various types of mouth sores associated with HIV, providing clear images and detailed descriptions. The goal is to empower patients and healthcare providers…
DMARDs for Rheumatoid Arthritis A Comprehensive Guide
DMARDs for rheumatoid arthritis are a crucial part of managing this chronic autoimmune disease. These disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs work to slow or halt the progression of the disease, improving quality of life for those affected. This guide explores the various types of DMARDs, their mechanisms of action, effectiveness, potential side effects, and treatment strategies, empowering…
Cast Decoration Ideas Transform Your Memories
Ideas for decorating your cast open up a world of creative possibilities. Whether it’s a child’s handprint, a pet’s paw, or a more elaborate creation, transforming a cast into a personalized artwork can be incredibly rewarding. From choosing the right materials to crafting unique designs, this guide will walk you through every step of the…