Understanding the role of progestin in birth control is crucial for informed decisions about reproductive health. This in-depth look explores the mechanisms by which progestin works, from its impact on ovulation and uterine lining to its influence on cervical mucus and potential effects on future fertility. We’ll also examine hormonal imbalances, combined birth control methods,…
Author: Ceasar Ritchie
How Long Does Postpartum Depression Last? Understanding the Journey
How long does postpartum depression last? This question weighs heavily on the minds of new mothers and their loved ones. It’s a complex journey, marked by a spectrum of experiences, and understanding the timeframe is crucial for navigating this challenging period. This article delves into the duration of postpartum depression (PPD), exploring the factors that…
Solu Medrol for MS A Comprehensive Guide
Solu Medrol for MS provides a potent anti-inflammatory approach to managing multiple sclerosis (MS). This guide delves into the intricacies of its use, from acute exacerbations to long-term management. Understanding the mechanisms of action, potential side effects, and patient considerations is crucial for effective treatment strategies. The article explores the role of inflammation in MS…
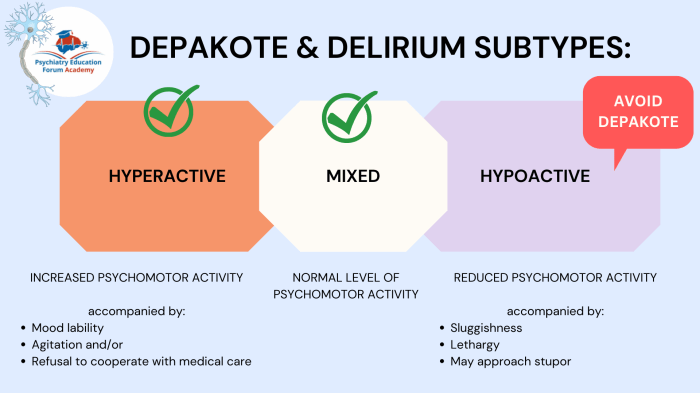
Whats the Difference Between Delirium and Dementia?
Whats the difference between delirium and dementia? These two conditions, though both affecting cognitive function, have vastly different characteristics, onsets, and courses. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Delirium typically emerges suddenly, often triggered by an underlying medical issue, and involves fluctuating attention and awareness. Dementia, on the other hand,…
Should I Take Vitamins During Cancer Treatment?
Should I take vitamins during cancer treatment? This crucial question weighs heavily on many facing cancer and their families. The nutritional needs of cancer patients are complex, often significantly altered by the disease and its treatments. This exploration delves into the intricate relationship between vitamins, cancer treatment, and overall well-being, offering a comprehensive overview of…
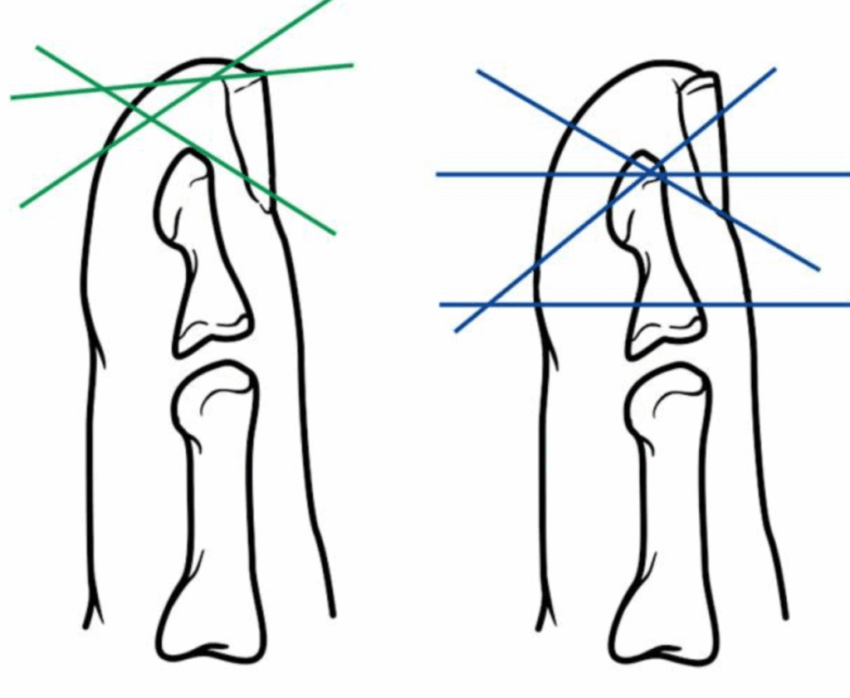
Fingertip Injury Will Tip Grow Back?
Fingertip injury will tip grow back? This in-depth exploration delves into the fascinating world of fingertip injuries, examining the intricate anatomy, diverse injury types, and the complex healing process. We’ll uncover the factors that influence regeneration, explore treatment options, and analyze the prognosis for full recovery. From the microscopic level of tissue repair to the…
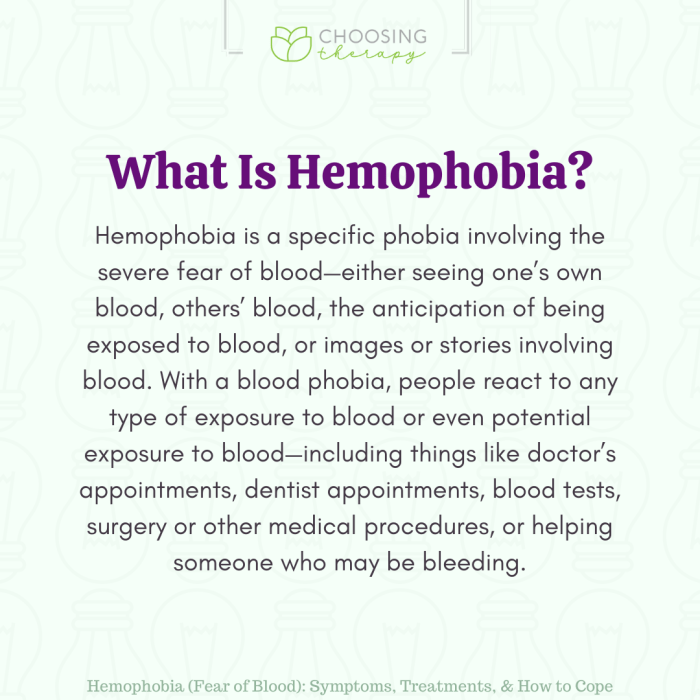
Hemophobia Fear of Blood Understanding and Coping
Hemophobia fear of blood – Hemophobia, fear of blood, is a specific phobia that can significantly impact a person’s life. This detailed exploration delves into the nuances of this condition, from its defining characteristics and symptoms to potential causes, effective treatments, and practical coping mechanisms. We’ll also examine the cultural and societal perspectives surrounding blood,…
Is Tramadol a Controlled Substance? Understanding the Details
Is tramadol a controlled substance? This question delves into the complexities of tramadol’s classification, legal status, and potential for misuse. We’ll explore its chemical composition, effects on the body, and legal regulations across various jurisdictions. Understanding the risks and benefits associated with this medication is crucial for both patients and healthcare professionals. Tramadol, a synthetic…
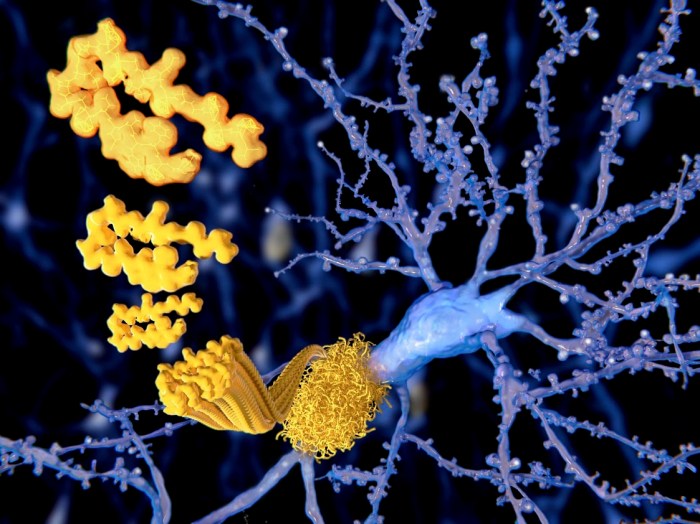
HATTR Amyloidosis with Polyneuropathy A Deep Dive
HATTR amyloidosis with polyneuropathy is a complex and often debilitating condition. This comprehensive look delves into the intricacies of this disease, exploring its underlying mechanisms, clinical presentation, diagnostic criteria, management strategies, prognosis, and the latest research. We’ll examine the challenges faced by patients and their families, and discuss the hope offered by current and future…
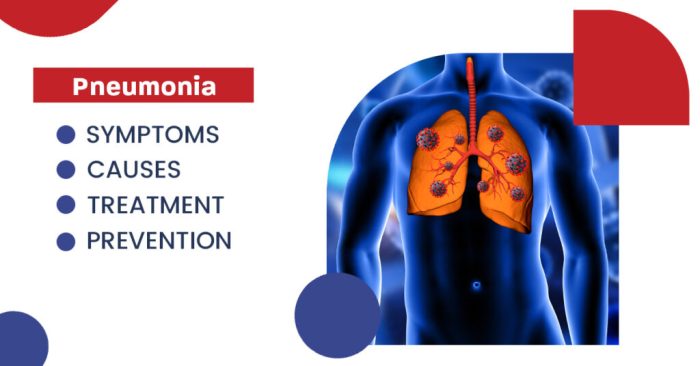
Pneumonia and COVID-19 A Deep Dive
Pneumonia and covid 19 – Pneumonia and COVID-19: This article delves into the complex interplay between these two respiratory illnesses. We’ll explore the shared symptoms, diagnostic challenges, and treatment strategies specific to patients experiencing both conditions. Understanding how pneumonia can complicate COVID-19 cases is crucial for healthcare professionals and those at risk. The co-occurrence of…