How to moisturize your scalp is crucial for healthy hair. A well-hydrated scalp leads to stronger, shinier, and more vibrant hair. This guide dives deep into understanding your scalp’s moisture needs, exploring various methods for hydration, from DIY treatments to commercial products. We’ll also examine lifestyle factors and how they impact scalp moisture, and finally,…
Author: Carlos Schuster
Scalp Psoriasis vs Dandruff A Comprehensive Guide
Scalp psoriasis vs dandruff: Understanding these seemingly similar scalp conditions is crucial for effective treatment. This guide dives deep into the differences, symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for both, allowing you to better manage your scalp health. From the initial symptoms to potential complications, we’ll explore everything you need to know to differentiate between…
Fear of Lizards Herpetophobia Explained
Fear of lizards herpetophobia – Fear of lizards, herpetophobia, is a fascinating and often misunderstood anxiety. It delves into the complex world of phobias, exploring the origins, triggers, and various manifestations of this specific fear. From the biological and psychological factors to the societal and cultural influences that shape our perceptions of these creatures, we’ll…
Omega 3 6 9 Your Bodys Essential Fats
Omega 3 6 9 fatty acids are vital components of a healthy diet, playing crucial roles in various bodily functions. These essential fats are categorized by their molecular structure and impact different aspects of our well-being. This comprehensive guide explores the diverse benefits, potential risks, and dietary sources of each type, from supporting heart health…
Outdoor Allergic Asthma Triggers A Comprehensive Guide
Outdoor allergic asthma triggers, a significant concern for many, encompass a range of environmental factors that can induce allergic reactions in asthmatics. Understanding these triggers, their mechanisms, and how to manage exposure is crucial for effective asthma management. This guide explores the various types of outdoor allergens, their seasonal patterns, and the environmental conditions that…
HAART Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy A Deep Dive
HAART highly active antiretroviral therapy has revolutionized HIV treatment, dramatically altering the course of the disease. This comprehensive look explores the science behind HAART, from its historical development and key components to its impact on patients’ lives. We’ll delve into the mechanisms of action, different treatment regimens, potential side effects, and the critical role of…
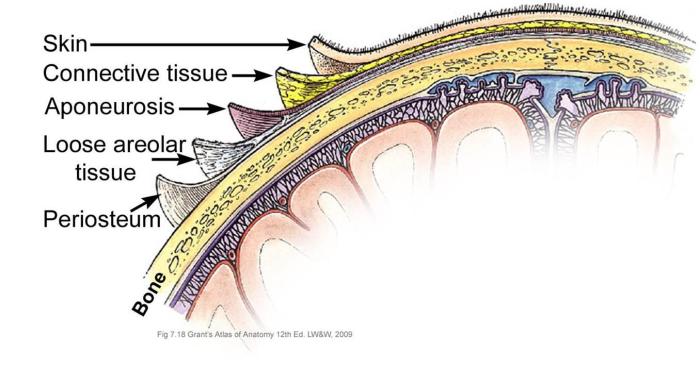
Understanding What is Discogenic Pain
What is discogenic pain? This deep dive explores the complexities of this often-misunderstood back pain, examining its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. We’ll uncover the anatomical structures involved, the differences between types of discogenic pain, and the various approaches to managing this condition. Discogenic pain, originating from the spinal discs, can manifest in a…
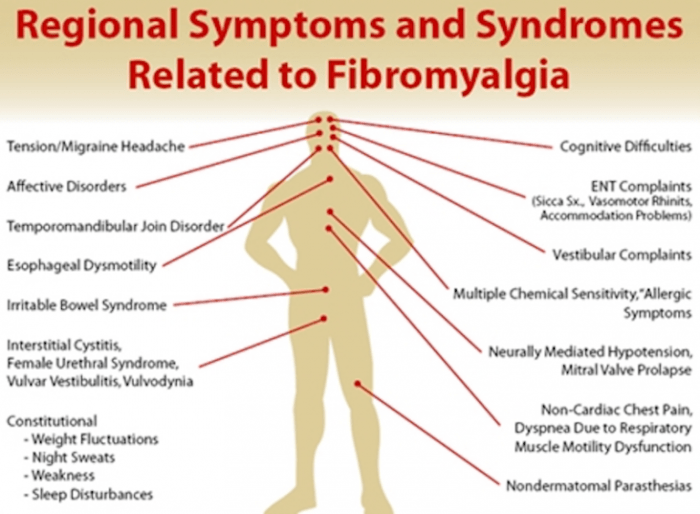
Fibromyalgia Primary or Secondary Unveiling the Types
Fibromyalgia primary or secondary is a complex condition that often stumps doctors and patients alike. Understanding the distinctions between primary and secondary forms is crucial for proper diagnosis and effective management. This exploration delves into the characteristics, causes, and treatment approaches for both, offering a comprehensive guide for anyone affected by or seeking to understand…
Signs Your Cold is Getting Better A Guide
Signs your cold is getting better are often subtle, but noticing them can bring a sense of relief and hope. This guide explores the key indicators that your body is successfully battling the cold, from early physical signs to improved energy levels and appetite. We’ll delve into the stages of recovery, helping you understand what’s…
Levels of Hospice Care A Comprehensive Guide
Levels of hospice care offer a spectrum of support for those facing end-of-life journeys. This guide delves into the nuances of these different levels, exploring the various services, eligibility criteria, and potential outcomes for patients and families. From basic care to more intensive support, understanding the different tiers of hospice care is crucial for making…