How does sleep inertia make it hard to wake up? This deep dive explores the physiological processes behind that sluggish feeling after waking. We’ll uncover the stages of sleep, neurochemical shifts, and how sleep deprivation amplifies this inertia. The result? A frustrating struggle to get going in the morning, impacting everything from concentration to mood.
We’ll investigate the common symptoms of sleep inertia, from sluggishness to impaired cognitive function, and examine the factors influencing its severity. Understanding these factors, like sleep duration and timing, is key to managing and mitigating this common sleep-related challenge.
Understanding Sleep Inertia
Sleep inertia, that groggy feeling after waking up, is more than just a nuisance. It’s a physiological response tied to the brain’s transition from sleep to wakefulness. Understanding the underlying mechanisms helps us appreciate the importance of adequate sleep and develop strategies to combat this common experience.Sleep inertia isn’t just about feeling sluggish; it’s a demonstrable decrease in cognitive function and performance.
The brain’s shift from the slow, synchronized activity of sleep to the active, varied patterns of wakefulness takes time, and this transition period is characterized by impaired cognitive abilities like attention, reaction time, and decision-making.
Physiological Processes of Sleep Inertia
Sleep inertia is a complex process involving multiple physiological systems. The brain’s transition from the slow-wave sleep (SWS) and rapid eye movement (REM) stages to wakefulness isn’t instantaneous. Instead, there’s a period of overlap where brain activity gradually shifts from sleep-specific patterns to the more complex, varied patterns associated with wakefulness. This gradual shift is responsible for the cognitive impairments often experienced upon waking.
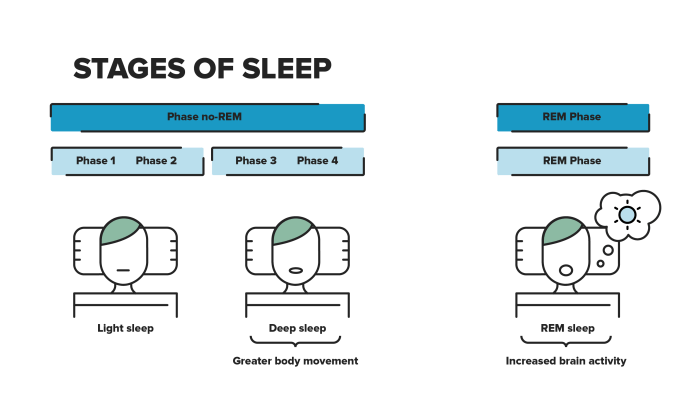
Stages of Sleep and Their Contribution to Sleep Inertia
Sleep progresses through distinct stages, each with unique characteristics that influence sleep inertia. The deeper stages of sleep, particularly slow-wave sleep (SWS), are associated with a greater degree of sleep inertia. This is because SWS is characterized by a high degree of brain synchrony and slow wave activity, requiring a longer transition period to reach a state of full wakefulness.
REM sleep, characterized by rapid eye movements and vivid dreams, also plays a role, although the exact mechanism is less clear than for SWS.
- Slow-wave sleep (SWS): Deep, restorative sleep characterized by slow brain waves. SWS is associated with the most pronounced sleep inertia, as the brain is at its lowest level of activity and needs a longer time to ramp up to wakefulness. It’s during SWS that the body repairs and restores itself, further emphasizing the importance of sufficient SWS for preventing sleep inertia.
- Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep: This stage is associated with dreaming and active brain activity. While REM sleep can contribute to sleep inertia, the effects are generally less pronounced than during SWS.
Neurochemical Changes During Sleep and Their Relation to Sleep Inertia
Neurochemical changes during sleep play a crucial role in sleep inertia. The balance of neurotransmitters like adenosine, which promotes sleep, and norepinephrine, which promotes wakefulness, shifts during the transition from sleep to wakefulness. The gradual increase in norepinephrine and the reduction in adenosine are essential for the restoration of full cognitive function.
Ugh, sleep inertia. It’s like my brain is still on vacation, resisting the siren call of the alarm clock. My body feels like lead, and my thoughts are foggy. Thankfully, there are topical medications like aldara for the treatment of nonmelanoma skin cancers aldara for the treatment of nonmelanoma skin cancers that can help with other types of sluggishness, but when it comes to waking up, it’s all about getting those Zzz’s! This sluggishness is a real drag, and it can really impact your day.
Honestly, I need a good night’s sleep to overcome sleep inertia.
- Adenosine: A neurochemical that accumulates during wakefulness and promotes sleep. As adenosine levels decrease upon waking, the brain slowly returns to a state of alertness.
- Norepinephrine: A neurotransmitter crucial for arousal and wakefulness. Its gradual increase upon waking helps facilitate the transition to full alertness.
Impact of Sleep Deprivation on Sleep Inertia
Sleep deprivation exacerbates sleep inertia. When sleep is insufficient, the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle is disrupted. This disruption affects the normal neurochemical balance and can lead to more pronounced and prolonged sleep inertia. The body has difficulty shifting from sleep to wakefulness, resulting in a more significant cognitive impairment.
Sleep Stage, Neurochemicals, and Effects on Wakefulness
| Sleep Stage | Neurochemicals | Effects on Wakefulness |
|---|---|---|
| Slow-Wave Sleep (SWS) | High adenosine, low norepinephrine | Significant sleep inertia; gradual transition to wakefulness |
| Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep | Moderate adenosine, moderate norepinephrine | Moderate sleep inertia; relatively quicker transition to wakefulness |
| Wakefulness | Low adenosine, high norepinephrine | Full alertness; optimal cognitive function |
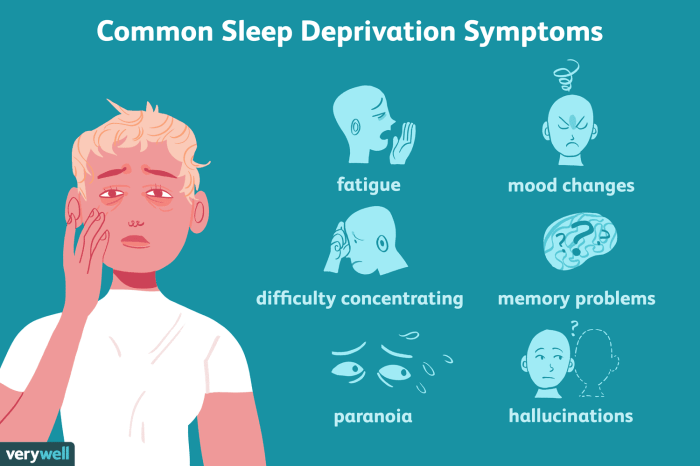
Symptoms and Effects of Sleep Inertia
Sleep inertia, that lingering grogginess after waking, isn’t just a mild inconvenience. It significantly impacts our daily functioning, affecting everything from our cognitive abilities to our emotional responses. Understanding these effects is crucial for recognizing the importance of adequate sleep and strategies to mitigate the negative impacts of sleep inertia.
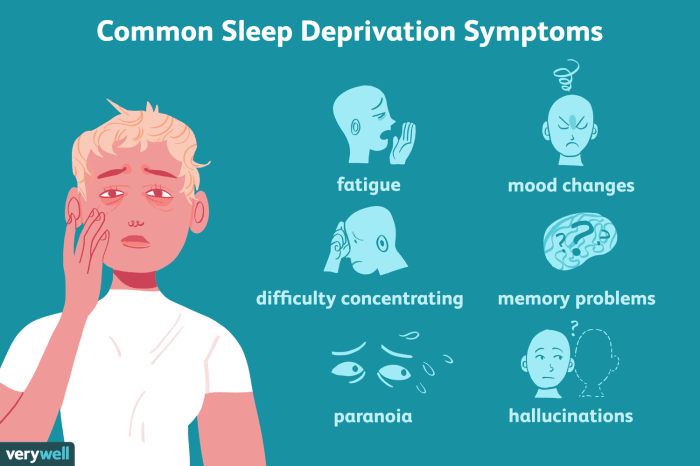
Common Symptoms of Sleep Inertia
Sleep inertia manifests in a range of symptoms, primarily impacting cognitive and emotional functions. These symptoms often peak immediately after waking and gradually diminish as the body adjusts. Recognizing these common symptoms can help individuals understand and address the effects of sleep inertia on their daily lives.
- Difficulty concentrating: The brain, still transitioning from the slow wave sleep, struggles to process information efficiently. This can manifest as difficulty focusing on tasks, mental fogginess, and a reduced ability to maintain attention.
- Slow reaction time: Sleep inertia directly affects the speed and accuracy of responses. The brain’s processing speed is reduced, potentially leading to slower reflexes and delayed reactions in various situations.
- Reduced alertness: The body’s natural alertness levels are suppressed during sleep inertia. This leads to feelings of drowsiness, lethargy, and a general lack of engagement with the environment. This can be especially noticeable in situations requiring high levels of vigilance.
Impact on Cognitive Performance
Sleep inertia negatively affects various cognitive functions. These impairments can impact daily tasks and responsibilities.
Ugh, sleep inertia – that groggy feeling after waking up. It’s like your brain is still on vacation, making it tough to get going. This sluggishness can sometimes mirror the discomfort of irritable bowel syndrome, where symptoms like cramping and bloating can also make it hard to get moving in the morning. Luckily, understanding the causes of sleep inertia, like a body’s delayed adjustment to waking up, can help you find solutions.
For more information on the various aspects of irritable bowel syndrome, check out this informative article: facts about irritable bowel syndrome. Ultimately, recognizing these factors can help us develop strategies to combat that post-sleep fog.
- Memory: The ability to encode and retrieve memories is compromised during sleep inertia. Individuals might experience difficulties remembering recent events or instructions. This can be problematic in situations requiring recall of specific information, such as attending meetings or carrying out detailed tasks.
- Problem-solving: The complex cognitive processes involved in problem-solving are hindered. Individuals might find it challenging to approach and solve problems logically and efficiently.
Impact on Mood and Emotional Regulation
Sleep inertia can also significantly affect emotional well-being. The brain’s emotional regulation centers are impacted, leading to mood swings and reduced emotional control.
- Irritability: The inability to process information efficiently can lead to feelings of frustration and irritability. Individuals might be more easily angered or agitated.
- Emotional lability: The brain’s emotional regulation system is disrupted, leading to unpredictable mood shifts. Individuals might experience rapid fluctuations in mood, from mild annoyance to intense anger.
Comparison with Other Sleep Disorders
While sleep inertia is a temporary phenomenon linked to waking from sleep, it differs from other sleep disorders.
- Sleep inertia is a temporary condition related to the transition from sleep to wakefulness, not a persistent issue.
- Other sleep disorders, like insomnia or sleep apnea, are characterized by persistent difficulties falling or staying asleep, and present different symptoms and underlying causes.
Severity Levels of Sleep Inertia Symptoms
The following table provides a general guideline for understanding the severity of sleep inertia symptoms. These levels are based on observed effects and are not a formal diagnostic tool.
| Symptom | Mild | Moderate | Severe |
|---|---|---|---|
| Difficulty concentrating | Slight difficulty focusing | Significant difficulty maintaining focus | Inability to concentrate on any task |
| Slow reaction time | Slightly slower response time | Noticeably slower response time | Markedly slow response time, putting oneself or others at risk |
| Reduced alertness | Mild drowsiness | Significant drowsiness and lethargy | Extreme drowsiness, impairing ability to function |
Factors Influencing Sleep Inertia
Sleep inertia, that groggy feeling after waking up, isn’t just a nuisance; it can significantly impact daily functioning. Understanding the factors contributing to this phenomenon helps us develop strategies to mitigate its effects and promote smoother transitions into our waking hours. Several key elements play a role in how easily we shed the sleep-fog, and these factors range from the obvious to the often-overlooked.
Sleep Duration and Quality
Sufficient sleep is fundamental for optimal cognitive function, and this includes a reduction in sleep inertia. Consistent sleep duration, typically 7-9 hours for adults, allows the brain to complete its restorative processes. Poor sleep quality, whether due to fragmented sleep, sleep disorders, or environmental factors, can lead to more pronounced sleep inertia. Individuals who regularly experience sleep deprivation or poor quality sleep may find it harder to fully wake up and transition into a state of alertness.
Sleep Timing and Chronotype
Our internal body clocks, known as chronotypes, influence when we feel most alert and sleepy. Early birds tend to experience less sleep inertia than night owls. Disrupting this natural rhythm, such as by changing sleep schedules or staying up late, can exacerbate the effects of sleep inertia. For example, forcing a night owl to wake up early for work may lead to greater sleep inertia compared to a morning person.
Impact of Sleep Disorders
Sleep disorders like insomnia and sleep apnea can significantly contribute to sleep inertia. Insomnia, characterized by difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, often results in poor sleep quality and prolonged sleep inertia. Sleep apnea, a condition where breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep, can lead to fragmented sleep and an increased susceptibility to sleep inertia. These sleep disruptions make it harder for the body and mind to transition from sleep to wakefulness.
Age and Individual Differences
Age plays a role in sleep inertia, with older adults sometimes experiencing more pronounced symptoms. This could be related to changes in sleep architecture and overall sleep quality that are common in aging. Individual differences also contribute to the experience of sleep inertia. Some individuals are simply more susceptible to sleep inertia than others, potentially due to genetic predispositions or other underlying factors.
For instance, a person with a pre-existing neurological condition might experience more pronounced sleep inertia compared to someone without such a condition.
Categorization of Factors Influencing Sleep Inertia
| Factor | Impact on Sleep Inertia |
|---|---|
| Sleep Duration and Quality | Reduced sleep duration and poor quality lead to more pronounced sleep inertia. Sufficient sleep duration and quality improve the transition from sleep to wakefulness. |
| Sleep Timing and Chronotype | Disruption of natural sleep-wake cycles can exacerbate sleep inertia. Individuals with chronotypes aligned with their schedules tend to have less sleep inertia. |
| Sleep Disorders (e.g., Insomnia, Sleep Apnea) | Fragmented sleep and disrupted sleep cycles due to sleep disorders increase sleep inertia. Effective treatment for sleep disorders can mitigate these effects. |
| Age and Individual Differences | Older adults may experience more pronounced sleep inertia due to changes in sleep patterns. Individual differences in susceptibility to sleep inertia exist. |
Strategies for Managing Sleep Inertia
Sleep inertia, that groggy feeling after waking up, can significantly impact our daily productivity and well-being. Understanding the factors that contribute to sleep inertia is crucial, but equally important is learning how to effectively manage its effects. This involves not only optimizing sleep quality and duration but also developing strategies to navigate the sluggishness and cognitive fog that often accompany waking up.
Optimizing Sleep Quality and Duration
Improving sleep quality and duration is fundamental to minimizing sleep inertia. A consistent sleep schedule, even on weekends, helps regulate the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle, known as the circadian rhythm. Aiming for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night is a common recommendation. Creating a relaxing bedtime routine, including a warm bath, reading, or meditation, can signal to the body that it’s time to wind down.
Avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bed is also crucial. A comfortable sleep environment, including a dark, quiet, and cool bedroom, can significantly improve sleep quality.
Managing Sleep Inertia Symptoms, How does sleep inertia make it hard to wake up
Several strategies can help manage the symptoms of sleep inertia. Gradual awakening is a common technique. Using an alarm clock that gradually increases in volume can ease the transition from sleep to wakefulness. Starting the day with light physical activity, such as a short walk or stretching, can help boost alertness. Hydration is also important; drinking a large glass of water upon waking can help rehydrate the body and improve alertness.
Finally, a light breakfast can provide the body with the energy needed to combat sleep inertia.
Strategies for Gradual Awakening
A gradual awakening approach is a key component in managing sleep inertia. This involves using a sunrise alarm clock or an alarm that gradually increases in volume to avoid abrupt awakenings. The transition from sleep to wakefulness is smoother, reducing the intensity of sleep inertia. By mimicking the natural light cycle, these methods reduce the sudden jolt that a typical alarm clock provides.
Lifestyle Modifications for Reduced Sleep Inertia
Lifestyle modifications can play a substantial role in reducing sleep inertia. Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, even on weekends, is critical for regulating the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle. This consistency helps to improve the quality of sleep and reduce the disruption caused by irregular sleep patterns. Avoiding caffeine and alcohol close to bedtime is essential, as these substances can interfere with the quality and duration of sleep.
Creating a relaxing bedtime routine can help signal the body that it’s time to wind down, promoting better sleep quality. Finally, ensuring a conducive sleep environment, free from distractions and disturbances, is crucial for a restful night’s sleep.
Ugh, sleep inertia. It’s like my brain is stuck in a fog after hitting snooze a few too many times. It’s seriously tough to get motivated and focused, and sometimes, it feels like my body’s just not cooperating. This sluggish feeling can sometimes be related to underlying health issues like thyroid problems, and a diet that avoids goitrogens, substances that can interfere with thyroid function, is often recommended.
A balanced diet with foods that support thyroid health, as detailed in the thyroid disease goitrogens diet , might help ease the struggle with sleep inertia. But in the end, consistent sleep hygiene practices are crucial to combating that post-sleep grogginess.
Comparing Management Approaches
Various approaches to managing sleep inertia exist. Gradual awakening methods, such as sunrise alarm clocks, offer a gentler transition out of sleep, reducing the intensity of sleep inertia. Lifestyle modifications, including a consistent sleep schedule and avoiding substances that interfere with sleep, contribute to improved sleep quality and reduced sleep inertia over time. While managing symptoms with immediate actions like hydration and light exercise can offer short-term relief, consistent sleep improvement is the most effective long-term solution.
Flowchart for Mitigating Sleep Inertia
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Establish a consistent sleep schedule, including weekends. |
| 2 | Create a relaxing bedtime routine to signal the body to wind down. |
| 3 | Ensure a conducive sleep environment (dark, quiet, cool). |
| 4 | Avoid caffeine and alcohol before bed. |
| 5 | Use a gradual awakening method (sunrise alarm, gradual volume increase). |
| 6 | Implement light physical activity upon waking. |
| 7 | Hydrate with a large glass of water upon waking. |
| 8 | Consume a light breakfast to provide energy. |
| 9 | Monitor and adjust the strategies as needed. |
Sleep Inertia and Daily Life: How Does Sleep Inertia Make It Hard To Wake Up
Sleep inertia, that groggy feeling after waking up, significantly impacts various aspects of daily life. It’s more than just a temporary inconvenience; it can impair cognitive function, reduce productivity, and even increase the risk of accidents. Understanding its influence on our daily routines is crucial for optimizing well-being and overall performance.
Impact on Work Productivity and Performance
Sleep inertia negatively affects work performance by diminishing alertness, concentration, and reaction time. Employees experiencing sleep inertia may struggle with tasks requiring complex problem-solving or quick decision-making. This can lead to decreased efficiency, increased errors, and ultimately, lower productivity. For example, a software developer experiencing sleep inertia might encounter more bugs in their code, or a customer service representative might respond less effectively to customer inquiries.
The decreased alertness and slowed cognitive processing lead to decreased productivity and performance.
Impact on Academic Performance and Learning
Students experiencing sleep inertia often face difficulties in absorbing new information and retaining it. Their cognitive functions are hampered, making it challenging to focus in class and participate actively in discussions. This can significantly impact their academic performance, especially in subjects requiring high levels of concentration and critical thinking. For instance, a student with sleep inertia might struggle to grasp complex concepts in a math class or recall information from a history lecture.
The decreased alertness and slowed cognitive processing lead to decreased academic performance.
Influence on Social Interactions and Relationships
Sleep inertia can affect social interactions negatively. Individuals experiencing it may appear irritable, less communicative, and less engaging in social situations. This can strain relationships and lead to misunderstandings. For example, a friend experiencing sleep inertia might appear less enthusiastic about a social gathering or have difficulty expressing their thoughts clearly, potentially leading to misunderstandings and conflicts.
The irritability and decreased communication skills lead to strained relationships and reduced social engagement.
Examples of Accidents or Mistakes Due to Sleep Inertia
Sleep inertia can contribute to accidents or mistakes in various contexts. A driver experiencing sleep inertia might make critical errors while operating a vehicle, such as drifting into another lane or failing to react to a sudden obstacle. A surgeon experiencing sleep inertia might make mistakes during a procedure due to decreased alertness and reaction time. A pilot experiencing sleep inertia might misinterpret instrument readings, potentially leading to an accident.
The decreased alertness and slowed reaction time lead to an increased risk of accidents and mistakes.
Effects of Sleep Inertia on Different Aspects of Daily Life
| Aspect of Daily Life | Examples | Impact Level |
|---|---|---|
| Work | Decreased efficiency, increased errors, reduced productivity | Moderate to High |
| Academics | Difficulty absorbing information, poor retention, reduced participation | Moderate to High |
| Social Interactions | Irritability, decreased communication, misunderstandings | Low to Moderate |
| Driving/Operating Machinery | Drifting, poor reaction time, misjudgment | High |
| Performing Complex Tasks | Surgical errors, software bugs, errors in financial reports | High |
Sleep Inertia and Specific Populations
Sleep inertia, the groggy feeling after waking up, isn’t experienced uniformly across all demographics. Individual differences in sleep patterns, physiological responses, and even environmental factors contribute to variations in how sleep inertia manifests and impacts different groups. Understanding these variations is crucial for developing targeted strategies to mitigate its negative effects.Different populations exhibit unique responses to sleep inertia, influencing their daily functioning and well-being.
Adolescents, for example, may struggle more with academic performance and social interactions, while older adults might find it harder to engage in physically demanding tasks. This section delves into these nuances and highlights how sleep inertia interacts with specific factors within different demographics.
Sleep Inertia in Adolescents
Adolescents experience significant hormonal and physiological changes, including altered sleep-wake cycles. This often leads to delayed sleep schedules, which can increase their vulnerability to sleep inertia. The impact of sleep inertia on adolescents extends beyond simply feeling tired. Their ability to concentrate in school, participate in extracurricular activities, and maintain healthy social relationships can be directly affected.
Studies have shown a correlation between insufficient sleep and poorer academic performance, and sleep inertia may be a contributing factor. Lack of adequate sleep also negatively affects their emotional regulation and overall well-being.
Sleep Inertia in Older Adults
Older adults often experience changes in sleep architecture, including decreased slow-wave sleep, which can affect their ability to fully recover during sleep. This can lead to increased susceptibility to sleep inertia and longer recovery times. The effects of sleep inertia on older adults may also be compounded by other age-related health conditions. It’s crucial to consider how sleep inertia might impact their independence and ability to perform daily tasks.
This includes activities like driving, social interaction, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Gender Differences in Sleep Inertia
While research on gender differences in sleep inertia is ongoing, some studies suggest potential variations in the experience. For instance, women might report experiencing sleep inertia more intensely or for longer durations than men. However, further research is needed to definitively understand these potential differences and the underlying biological and social factors.
Sleep Inertia and Mental Health Conditions
Sleep inertia can exacerbate existing mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety. The lack of alertness and cognitive function associated with sleep inertia can make it challenging to engage in coping mechanisms and maintain a positive outlook. Individuals with pre-existing mental health conditions may require extra support and tailored strategies to manage sleep inertia and its impact on their well-being.
Sleep Inertia and Professions Requiring Alertness
Individuals in professions requiring high levels of alertness, such as air traffic controllers, surgeons, and truck drivers, are particularly vulnerable to the negative effects of sleep inertia. Reduced alertness and cognitive performance can have serious consequences in these roles, potentially leading to accidents or errors. Proper sleep hygiene and strategies to mitigate sleep inertia are crucial for maintaining safety and efficiency in these demanding occupations.
Sleep Inertia Across Demographics
| Demographic Group | Potential Impacts of Sleep Inertia | Possible Contributing Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Adolescents | Reduced academic performance, difficulty concentrating, impaired social interactions | Delayed sleep schedules, hormonal changes, increased social demands |
| Older Adults | Reduced ability to perform daily tasks, slower reaction times, increased risk of falls | Changes in sleep architecture, age-related health conditions |
| Individuals with Mental Health Conditions | Exacerbation of symptoms, reduced ability to cope, increased emotional distress | Disrupted sleep patterns, underlying mental health issues |
| Professionals Requiring Alertness | Increased risk of accidents, errors, decreased efficiency | Shift work, irregular sleep schedules, demanding work environments |
| Women | Potentially more intense or prolonged experience of sleep inertia | Biological factors, social and lifestyle factors (still under investigation) |
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, sleep inertia is a significant factor affecting daily life, impacting everything from work productivity to social interactions. Understanding its underlying causes, symptoms, and potential solutions is crucial for improving overall well-being. By implementing strategies for better sleep hygiene and managing individual sleep patterns, we can combat the negative effects of sleep inertia and achieve a more productive and fulfilling daily experience.