Symptoms of dehydration in elderly individuals often present differently than in younger adults, making recognition crucial. This article delves into the various signs, from common to uncommon, highlighting the impact of underlying health conditions and offering strategies for prevention and management. Understanding how dehydration manifests in older adults is vital. Factors like decreased thirst sensation,…
Author: Anastacio Bogisich
Ways to Stop a Cough Your Comprehensive Guide
Ways to stop a cough—a persistent, irritating issue that can disrupt your daily life. This comprehensive guide delves into various approaches, from understanding the different types of coughs and their causes, to exploring effective home remedies, over-the-counter medications, and lifestyle adjustments. We’ll also discuss when to seek medical attention and preventative strategies to keep coughs…
Breastfeeding Supplements What Works & Choosing Wisely
Supplements for breastfeeding what works and how to choose the right ones can be confusing. This guide dives deep into the world of breastfeeding supplements, exploring the potential benefits, risks, and crucial considerations for new mothers. We’ll uncover which supplements might truly support your journey and how to evaluate them safely and effectively. From understanding…
The Benefits of Emu Oil A Deep Dive
The benefits of emu oil are multifaceted, extending from skincare to potential health applications. Derived from the emu, a large flightless bird native to Australia, this natural oil has garnered significant interest for its purported moisturizing and healing properties. From reducing scars to soothing inflammation, emu oil’s versatility is truly remarkable. This exploration delves into…
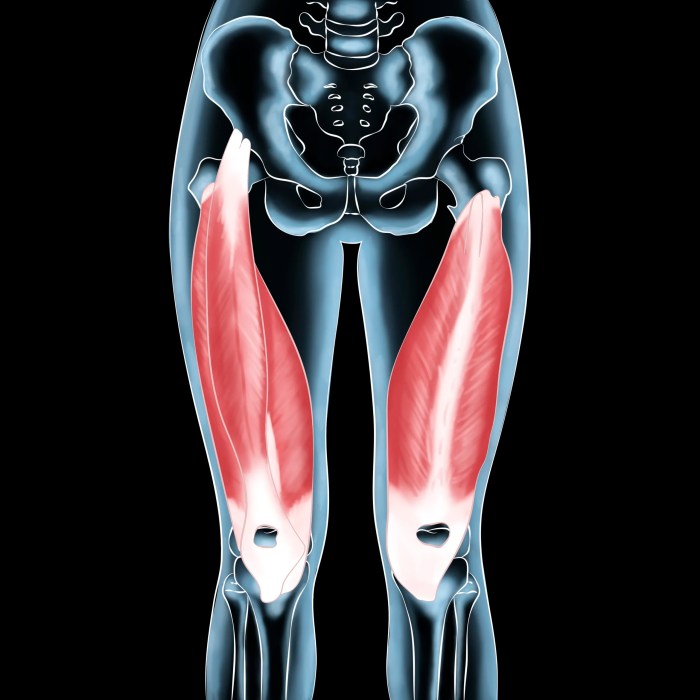
What are the Quadriceps Muscles? A Deep Dive
What are the quadriceps muscles? They’re a powerful group of muscles located at the front of your thighs, crucial for knee extension and a wide range of movements. This comprehensive guide delves into their anatomy, function, clinical significance, and more. From their individual components to their role in daily activities, we’ll explore everything you need…
Stinging Nettle Everything You Need to Know
Stinging nettle everything you need to know dives deep into the fascinating world of this often-overlooked plant. From its historical uses and cultural significance to its potential health benefits and culinary applications, we’ll explore every aspect of this remarkable species. Discover how to identify stinging nettle from similar plants, understand its unique stinging mechanism, and…
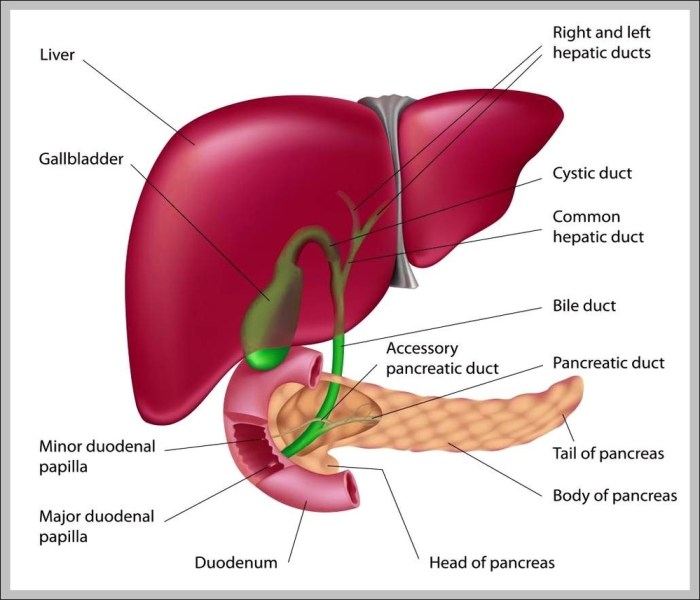
Gallbladder Anatomy, Function, and Treatment
The gallbladder anatomy function and treatment is a crucial topic for understanding digestive health. This exploration delves into the gallbladder’s role in the human body, from its intricate structure to the various disorders that can affect it. We’ll cover everything from its location and function in the digestive process to the different treatment options available…
What You Need to Know About Valerian A Deep Dive
What you need to know about valerian is a comprehensive exploration of this herbal remedy. From its historical use to its potential benefits and risks, we’ll uncover everything you need to make informed decisions about incorporating valerian into your wellness routine. We’ll delve into its origins, forms, potential benefits for sleep, anxiety, and stress, and…
Turmeric Health Benefits for Women A Deep Dive
Turmeric health benefits for women are plentiful and fascinating, offering a natural approach to overall well-being. From hormonal balance to digestive health, bone strength, skin radiance, and immune support, turmeric’s active compound, curcumin, appears to play a key role in various aspects of women’s health. This exploration delves into the science behind turmeric’s effects, highlighting…
Fall Produce for Brain Health Boosting Cognition
Fall produce for brain health is a delicious way to support your cognitive function. From the crisp crunch of apples to the warm, comforting flavors of pumpkins and sweet potatoes, these seasonal delights are packed with nutrients that can improve memory, focus, and overall brainpower. This exploration dives into the nutritional powerhouse of fall produce…