Coffee brewing method cholesterol: Different ways to brew coffee can affect how your body processes cholesterol. This exploration dives into various brewing methods, examining their impact on the compounds in coffee that may influence cholesterol levels. From the familiar drip coffee to the nuanced pour-over, we’ll uncover how each method extracts different components and potentially…
Author: admin
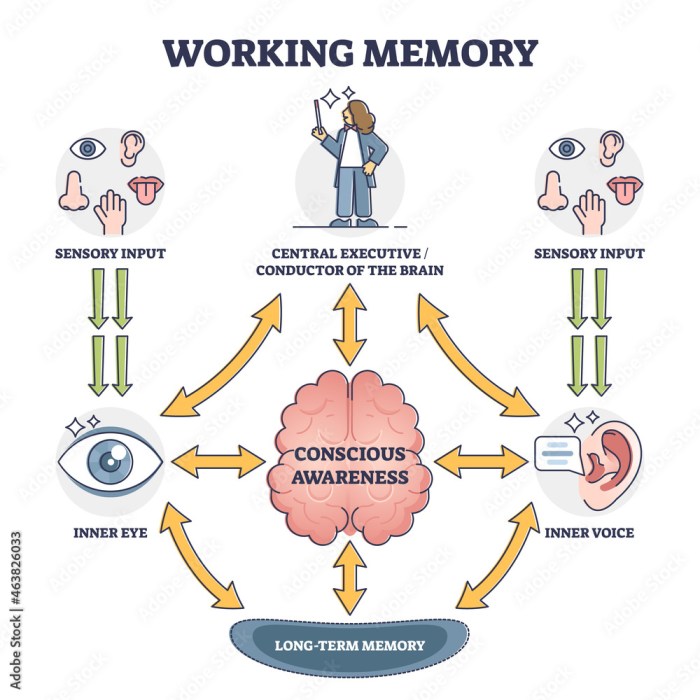
Memory Tip 1 Keyword Mnemonics
Memory tip 1 keyword mnemonics – Memory tip 1: mnemonics is a powerful technique for memorizing information by associating s with concepts. Imagine vividly linking words or phrases to images and locations. This method taps into the brain’s natural ability to form connections, making learning and recall effortless. It’s more than just rote memorization; it’s…
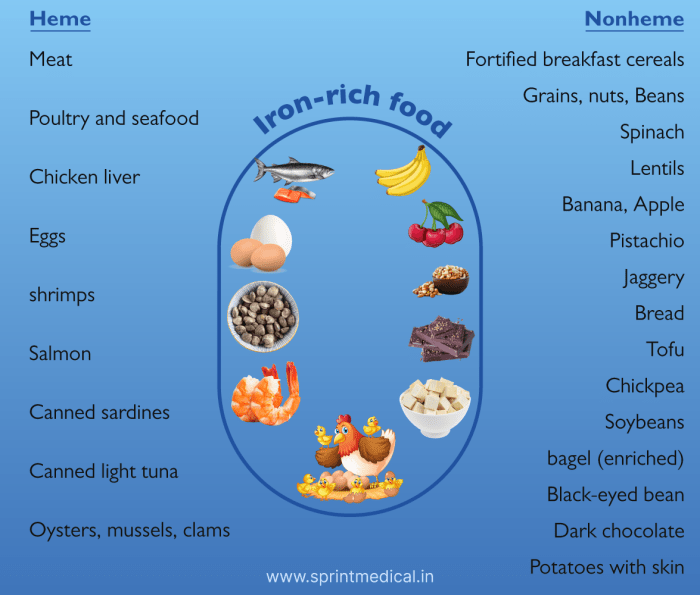
Foods and Drinks to Avoid for Weight Loss
Foods and drinks to avoid for weight loss are crucial for successful weight management. This guide dives deep into the world of nutrition, exploring the detrimental effects of certain foods and beverages on your weight loss journey. From sugary drinks to processed meals, we’ll uncover hidden pitfalls and provide practical alternatives for a healthier lifestyle….
Recording Family Medical History A Guide
Recording family medical history sets the stage for proactive health management. This detailed guide explores the crucial importance of documenting family health information, from understanding its significance to practical methods for collection, storage, and sharing. It will equip you with the knowledge and tools to create a comprehensive family health record, empowering you to make…
Best Time to Take Collagen Your Absorption Guide
Best time to take collagen sets the stage for a deep dive into optimizing your collagen supplement routine. Understanding how your body absorbs collagen is key to maximizing its benefits. Factors like meal timing, blood sugar levels, digestive health, and even the specific form of collagen you choose all play a role in how effectively…
How to Shrink Fibroids A Comprehensive Guide
How to shrink fibroids? This comprehensive guide delves into the various methods, medical treatments, and lifestyle adjustments that can help manage and potentially reduce fibroid size. We’ll explore the science behind fibroids, from their causes and diagnosis to the potential benefits and drawbacks of different approaches. Understanding the complexities of fibroids is crucial for anyone…
Vitiligo vs Albinism Whats the Difference?
Vitiligo vs albinism what s the difference – Vitiligo vs albinism: what’s the difference? This exploration delves into the distinct characteristics, underlying mechanisms, and impacts of these conditions. Understanding the nuances between vitiligo and albinism is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective support. We’ll examine their physical manifestations, genetic origins, and the challenges faced by…
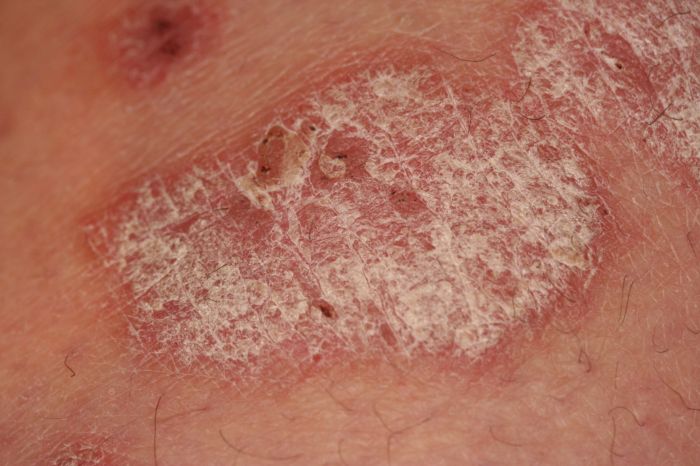
Psoriasis and Your Life A Deep Dive
Psoriasis and your life intertwine in profound ways, impacting everything from daily routines to emotional well-being. This exploration delves into the multifaceted nature of living with psoriasis, offering insights into its effects, treatment options, and the importance of coping strategies. We’ll navigate the challenges and triumphs of managing this condition, emphasizing the journey of adaptation…
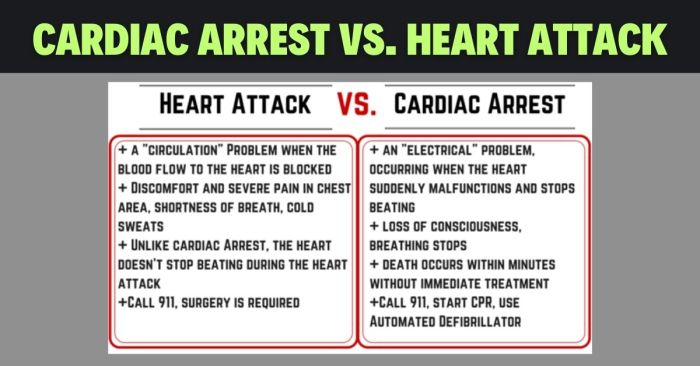
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) A Deep Dive
Cardiac resynchronization therapy crt – Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) is a powerful intervention for patients with heart failure. It aims to correct the electrical timing issues in the heart, leading to improved pumping efficiency. This therapy utilizes specialized devices to resynchronize the heart’s chambers, restoring a coordinated heartbeat. Different types of CRT devices exist, each…
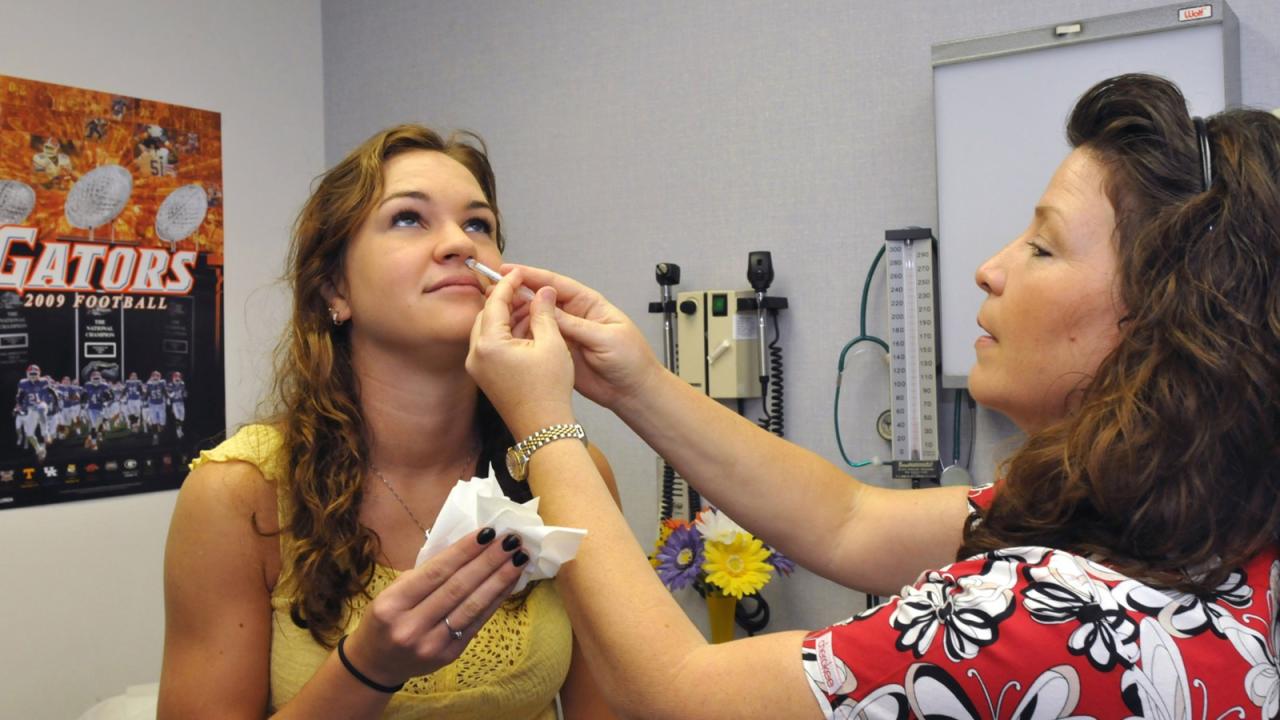
What is the Nasal Flu Vaccine Flumist? A Deep Dive
What is the nasal flu vaccine Flumist? This guide dives deep into the nasal spray flu vaccine, exploring its form, benefits, safety, and effectiveness compared to other options. We’ll uncover how it works, who it’s best for, and what to expect from its administration and potential side effects. Prepare to be well-informed! Flumist is a…