Rheumatoid arthritis in the neck can significantly impact your quality of life, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Understanding the specific ways RA affects the cervical spine, along with its symptoms and treatment options, is crucial for effective management. This guide delves into the complexities of rheumatoid arthritis in the neck, providing a comprehensive overview…
Author: admin
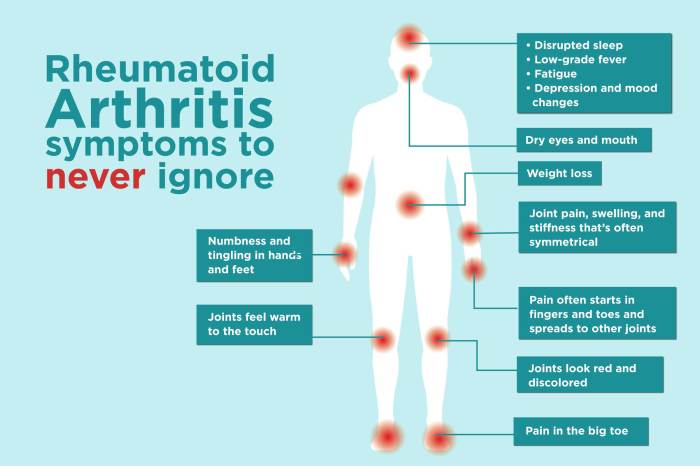
Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis Flares A Deep Dive
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis flares sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into the complexities of this chronic condition. We’ll explore the various symptoms, their progression, and triggers, shedding light on how flares impact daily life. Understanding these nuances is crucial for effective management and improved quality of life. This comprehensive…
How Long Does Alcohol Stay in Urine? A Deep Dive
How long does alcohol stay in urine? This question is crucial for various reasons, from understanding the effects of alcohol consumption on the body to navigating legal and health implications. The duration of alcohol detection in urine is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including individual metabolism, the type of alcohol consumed, and the…
Reverse Walking in Physical Therapy A Deep Dive
Reverse walking in physical therapy is a powerful technique gaining traction for improving balance, gait, and strength. This approach challenges the typical forward motion, offering unique benefits for various patient populations. We’ll explore the biomechanics, benefits, and safety considerations, along with exercise progressions and modifications. This comprehensive guide dives into the specifics of reverse walking,…
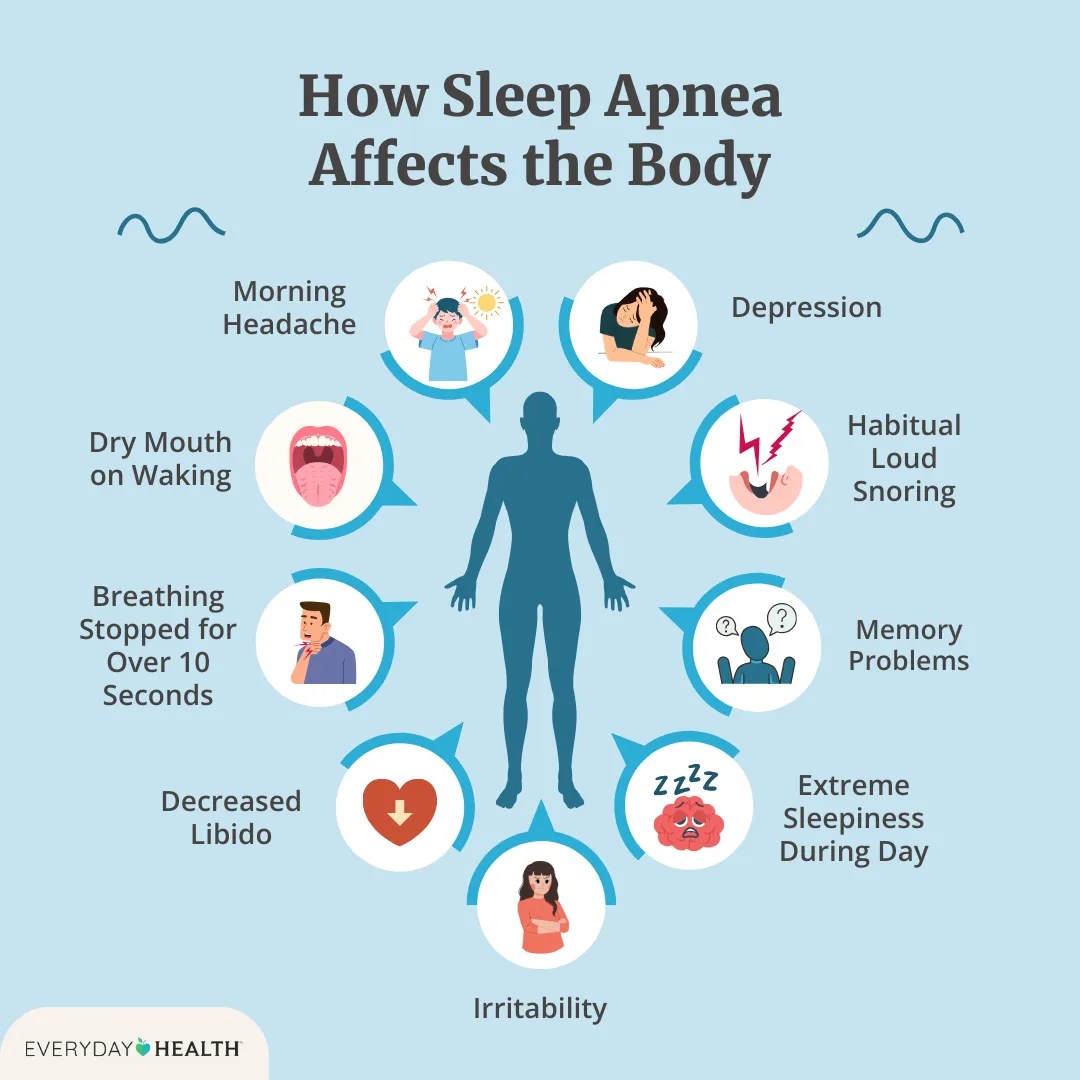
Effects of Sleep Apnea A Deep Dive
Effects of sleep apnea extend far beyond just feeling tired. This comprehensive exploration delves into the various ways sleep apnea impacts your overall health, from the cardiovascular system to cognitive function. We’ll uncover the different types, symptoms, and potential long-term consequences of this often-overlooked condition. Understanding these effects is crucial for early detection and effective…
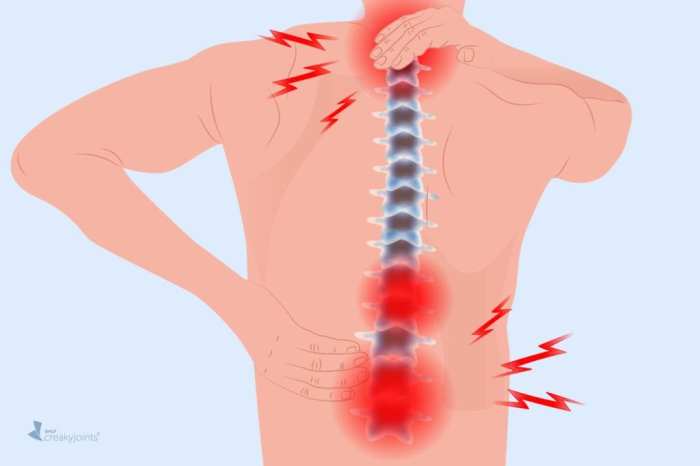
Rheumatoid Arthritis Back Pain Understanding the Impact
Rheumatoid arthritis back pain is a complex condition that significantly impacts a person’s life. It’s not just about aches and stiffness; it’s about understanding the underlying mechanisms, the various symptoms, and the available treatment options. This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of RA back pain, providing a detailed overview of its causes, diagnosis, and…
How to Exfoliate Your Scalp for Clean Healthy Hair
How to exfoliate your scalp for clean healthy hair? This comprehensive guide dives deep into the world of scalp care, revealing secrets to unlocking vibrant, luscious locks. From understanding different scalp types to choosing the perfect exfoliating agents, we’ll explore the entire process, ensuring you’re well-equipped to maintain a healthy and happy scalp. We’ll cover…
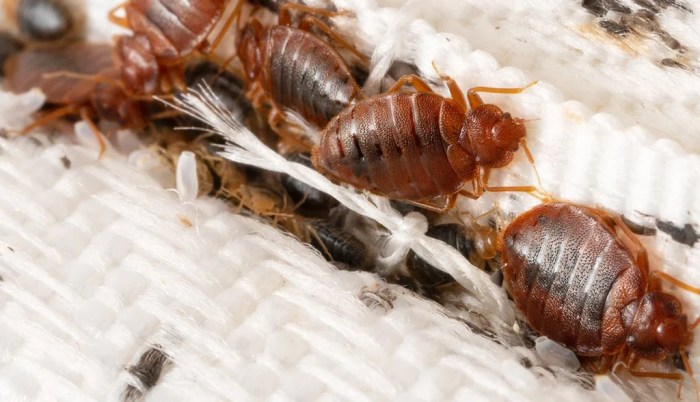
What Causes Bed Bugs A Deep Dive
What causes bed bugs? This isn’t just a pest problem; it’s a complex interplay of environmental factors, human behavior, and the very nature of these tiny bloodsuckers. From the seemingly innocuous to the downright disturbing, understanding the reasons behind a bed bug infestation is key to prevention and effective control. We’ll explore everything from the…
Weight Loss Reverses Type 2 Diabetes
Weight loss reverse type 2 diabetes is a powerful concept, showing how shedding pounds can dramatically improve health. This journey involves understanding the mechanisms linking obesity to diabetes, learning about effective weight loss strategies, and the vital role of lifestyle modifications. From dietary approaches to exercise and stress management, this exploration will guide you through…
Watercress Benefits A Nutrition Profile
Watercress benefits and nutrition profile sets the stage for an exploration of this vibrant leafy green. From its historical uses to its modern-day health advantages, we’ll delve into the nutritional value, potential health benefits, and various ways to enjoy this versatile ingredient. Discover the surprising wealth of nutrients packed within each bite. This comprehensive guide…