Sotatercept pulmonary arterial hypertension is a significant advancement in the fight against this often-deadly disease. This exploration delves into the specifics of this treatment, examining its mechanism of action, clinical trial data, and the impact it has on patient outcomes. We’ll also look at potential side effects and the exciting future of PAH treatment. Understanding…
Author: admin
Early Stage Toenail Fungus A Guide
Early stage toenail fungus is a common condition that often goes unnoticed in its initial stages. This guide dives into the specifics, from recognizing the early symptoms and causes to understanding preventative measures, diagnostic methods, and treatment options, including home remedies. We’ll explore everything from visual comparisons of healthy and infected nails to detailed tables…
Flovent, Qvar, Pulmicort, Alvesco, or Asmanex A Deep Dive
Flovent qvar pulmicort alvesco or asmanex – Flovent, Qvar, Pulmicort, Alvesco, or Asmanex – these inhaled corticosteroids are frequently prescribed for respiratory conditions. Understanding their similarities and differences, mechanisms of action, and potential side effects is crucial for informed decision-making. This comprehensive guide dives into each medication, comparing their effectiveness, usage, and considerations for patients….
Gallbladder Removal Digestive Issues Explained
Digestive problems after gallbladder removal are a common concern for patients. This comprehensive guide delves into the potential issues, symptoms, diagnoses, treatments, and dietary considerations. Understanding the physiological changes and potential complications following cholecystectomy is crucial for effective management. The gallbladder plays a vital role in the digestion of fats. When it’s removed, the body…
Antibiotics Before Dental Work A Guide
Antibiotics before dental work are a common practice, but understanding the reasons behind it and the potential alternatives is crucial. This guide delves into the rationale for using antibiotics before dental procedures, considering various factors and risks involved. We’ll examine the different types of dental work, the impact of patient history, and alternatives to routine…
How Long Do Short People Live? Unveiling the Truth
How long do short people live? This question delves into the complex relationship between height, health, and lifespan. While simple correlations might appear, a deeper exploration reveals the interwoven factors of genetics, environment, culture, and societal influences. The narrative explores a range of perspectives, from defining “short” across demographics and time periods to examining potential…
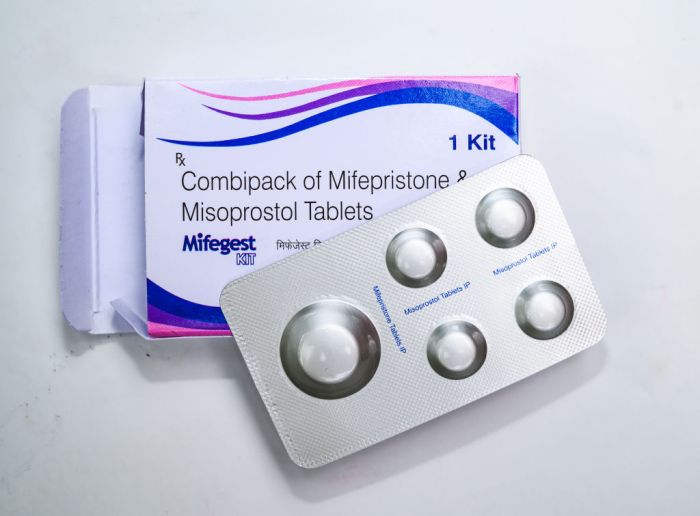
RU486 the Abortion Pill A Comprehensive Guide
RU486 the abortion pill, a medical method for terminating a pregnancy, involves a specific process and raises various considerations. This guide delves into the intricacies of this procedure, from its mechanism of action to the patient experience and ethical implications. The pill, mifepristone, works by blocking the hormone progesterone, which is essential for maintaining a…
Swimming for Weight Loss Your Aquatic Journey
Swimming for weight loss is a fantastic way to shed pounds and sculpt a healthier you. It’s a low-impact exercise that’s easy on the joints, making it ideal for all fitness levels. This comprehensive guide dives deep into the world of aquatic workouts, exploring the science behind calorie burning, various swimming strokes, effective workout plans,…
Are My Health Insurance Premiums Tax Deductible?
Are my health insurance premiums tax deductible? This question is crucial for anyone managing their finances, especially during these times. Understanding the complexities surrounding tax deductions for health insurance premiums can significantly impact your bottom line. This guide delves into the nuances of deductibility, examining various scenarios, tax forms, and legal considerations to help you…
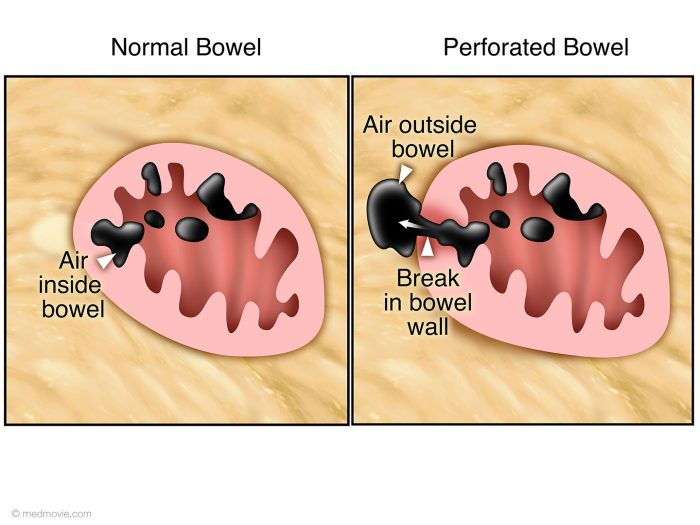
Whats a Bowel Perforation? A Deep Dive
Whats a bowel perforation – What’s a bowel perforation? It’s a serious medical condition where a hole develops in the wall of the intestines. This can happen spontaneously, due to trauma, or various underlying conditions like inflammatory bowel disease. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments is crucial for anyone seeking knowledge about this potentially life-threatening…