Cardiac effects of obesity medications are a crucial area of study, as these drugs can potentially impact the cardiovascular system. This blog post explores the different classes of obesity medications currently available, examining their mechanisms of action and potential physiological pathways through which they might affect the heart. We’ll delve into the potential cardiac risks associated with each class, analyzing the evidence supporting these risks and the underlying mechanisms.
Factors influencing these effects, such as patient demographics and pre-existing conditions, will also be considered. The information presented here aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of this complex relationship.
This exploration includes a detailed table comparing the various classes of obesity medications, highlighting their mechanisms of action, potential cardiac effects, and areas needing further research. A second table summarizes potential cardiac risks, their severity, and the supporting evidence. A third table explores the factors that influence the cardiac effects, analyzing their impact on different medication classes. Understanding these complexities is crucial for both patients and healthcare professionals to make informed decisions regarding obesity management.
Introduction to Obesity Medications and Cardiac Effects: Cardiac Effects Of Obesity Medications
Obesity is a significant health concern, contributing to various cardiovascular complications. Consequently, pharmaceutical interventions aimed at weight loss have become increasingly important. These medications, however, come with the potential for cardiac side effects, necessitating careful consideration and ongoing research. This discussion delves into the diverse classes of obesity medications, their mechanisms of action, and their potential impact on the cardiovascular system.Understanding the interplay between these medications and cardiac health is crucial for both patient safety and effective treatment strategies.
Recent studies on the cardiac effects of obesity medications have sparked a lot of discussion. Understanding these potential side effects is crucial for anyone considering these treatments. Ultimately, a healthy lifestyle, combined with a strong sense of self-worth, which is directly related to what is self esteem , is often the most effective approach to managing weight and overall well-being.
This approach can ultimately contribute to healthier hearts and better long-term outcomes in relation to the cardiac effects of these medications. The focus on self-care and confidence is often overlooked when discussing medical interventions.
Clinicians and patients alike need a clear understanding of the potential risks and benefits associated with these drugs.
Overview of Obesity Medication Classes
Currently available obesity medications span various mechanisms of action. Some medications target appetite regulation, while others focus on influencing fat absorption or metabolism. This diversity of approaches highlights the complexity of obesity and the need for multiple therapeutic strategies.
Mechanisms of Action of Obesity Medications
The mechanisms of action vary widely among different obesity medications. Some drugs, for example, act on the central nervous system to suppress appetite. Others impact the gastrointestinal tract to alter nutrient absorption. A third group influences metabolism, potentially impacting energy expenditure.
Potential Physiological Pathways for Cardiac Effects, Cardiac effects of obesity medications
These medications can impact the cardiovascular system through several physiological pathways. For instance, changes in blood pressure, heart rate, or lipid profiles are potential consequences of altering appetite, metabolism, or gut function. Further, some medications may indirectly influence inflammation and clotting, potentially increasing cardiovascular risk.
Comparison of Obesity Medication Classes
| Medication Class | Mechanism of Action | Potential Cardiac Effects | Further Research Needed |
|---|---|---|---|
| GLP-1 Receptor Agonists | Mimic the effects of glucagon-like peptide-1, a hormone that regulates blood sugar and appetite. Often associated with improved insulin sensitivity and reduced appetite. | Potential for increased heart rate and blood pressure in some individuals, though generally well-tolerated. Studies suggest a positive impact on cardiovascular risk factors in some cases. | Long-term cardiovascular outcomes, particularly in individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions. Specific impact on different cardiovascular risk factors. |
| Semaglutide (a GLP-1 RA) | A specific GLP-1 receptor agonist, known for its potent appetite-suppressing and blood sugar-regulating effects. | Reported cases of increased heart rate and blood pressure, although these are often mild and transient. Studies are ongoing to fully evaluate the long-term cardiovascular safety profile. | Specific effects on different heart conditions, and interactions with other medications. |
| Lipase Inhibitors | Reduce the absorption of dietary fats in the gut, leading to decreased caloric intake. | Potential for mild gastrointestinal side effects like diarrhea and abdominal cramps, but cardiovascular effects are generally considered minimal. | Long-term effects on lipid profiles and cardiovascular health in different patient populations. Potential for interactions with other medications. |
| Amphetamine-like Medications | Increase central nervous system activity, reducing appetite and increasing energy expenditure. | Potential for increased heart rate and blood pressure, and possible cardiac arrhythmias. Associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular adverse events compared to other classes. | Long-term effects on cardiovascular structure and function. Optimal patient selection criteria. |
Potential Cardiac Risks Associated with Obesity Medications
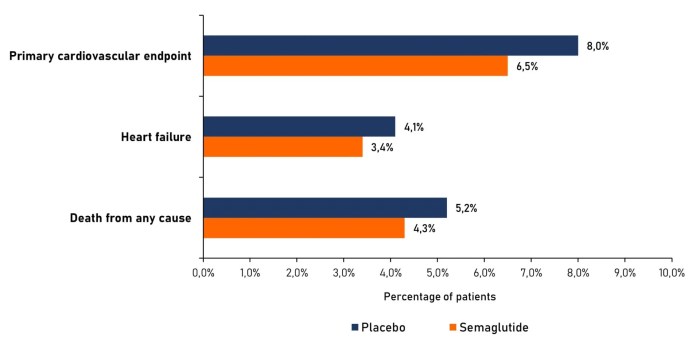
Navigating the world of obesity medications is a delicate balancing act. While these drugs can be incredibly helpful in managing weight, potential cardiac side effects are a significant concern. Understanding the potential risks associated with each class of medication is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. This exploration dives into the potential cardiovascular complications, examining the evidence and underlying mechanisms.
Potential Adverse Cardiovascular Effects by Medication Class
Obesity medications target different pathways to achieve weight loss, and these differing mechanisms can lead to distinct cardiac risks. It’s essential to acknowledge that not all individuals will experience these side effects, and careful monitoring is key.
Recent research into the cardiac effects of obesity medications is fascinating, but it’s crucial to consider the bigger picture. For example, studies like the cellular aging cancer study highlight the complex interplay between cellular aging and disease. Ultimately, understanding how these medications impact the heart requires a holistic view, encompassing not just immediate cardiac effects, but also the long-term consequences on cellular health.
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
These medications, often prescribed for type 2 diabetes as well, stimulate the release of insulin and suppress glucagon. While generally considered safe, potential cardiac risks include palpitations, tachycardia, and a slight increase in blood pressure. Evidence suggests that these effects are usually mild and transient, but careful monitoring is essential. Some studies suggest a potential link between prolonged use and a slight increase in heart rate variability, though the clinical significance of this remains under investigation.
Semaglutide (Wegovy)
A specific GLP-1 receptor agonist, semaglutide, has garnered significant attention. While generally well-tolerated, reported cases of atrial fibrillation (irregular heartbeat) have emerged. The exact relationship between semaglutide and atrial fibrillation is still being studied, and further research is necessary to definitively establish a causal link.
Amphetamines and Similar Medications
These medications can increase heart rate and blood pressure. The evidence supports this effect, and the potential for exacerbating existing cardiovascular conditions is significant. The underlying mechanism involves the sympathomimetic effects of these drugs, stimulating the sympathetic nervous system. Caution is crucial for patients with pre-existing heart conditions.
Other Medication Classes
Other classes of obesity medications, such as those targeting appetite suppressants or lipase inhibitors, also present potential cardiac risks. These risks are often less well-documented compared to GLP-1 receptor agonists, and further research is needed to fully understand the spectrum of potential effects.
While researching the cardiac effects of obesity medications, I stumbled upon some interesting connections. These medications can sometimes have surprising side effects, and understanding how they impact the heart is crucial. For instance, some individuals taking these medications have reported experiencing symptoms that mirror those of stroke, including numbness or weakness, particularly in women. Knowing the potential symptoms of stroke, especially in women, is essential.
For more detailed information on recognizing stroke symptoms in women, check out this helpful resource: stroke symptoms in women. Ultimately, ongoing research into the cardiac effects of these medications is vital to ensure patient safety.
Summary Table of Potential Cardiac Risks
| Medication Class | Potential Cardiac Risk | Severity of Risk | Evidence Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| GLP-1 Receptor Agonists | Palpitations, tachycardia, slight blood pressure increase, potential increase in heart rate variability | Generally mild and transient | Moderate |
| Semaglutide (Wegovy) | Atrial fibrillation | Potential for serious complications | Emerging |
| Amphetamines and Similar | Increased heart rate and blood pressure | Potentially significant, particularly in individuals with existing heart conditions | Strong |
| Other Classes (e.g., Appetite Suppressants, Lipase Inhibitors) | Less well-documented cardiac risks; further research needed | Unknown | Limited |
Factors Influencing Cardiac Effects of Obesity Medications

Obesity medications, while potentially beneficial for weight management, can pose cardiac risks. Understanding the factors that influence these effects is crucial for tailoring treatment strategies and identifying high-risk patients. Different mechanisms of action in various medication classes contribute to the diverse range of potential cardiac impacts.Several factors significantly influence the cardiac effects of obesity medications. Patient characteristics, pre-existing conditions, and medication-specific properties all play a role in determining individual responses.
Patient Characteristics and Pre-existing Conditions
Patient age, gender, and overall health status are important factors. Older adults and individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions, such as hypertension or coronary artery disease, may exhibit heightened sensitivity to cardiac side effects. Furthermore, co-morbidities like diabetes and sleep apnea can interact with obesity medications, potentially amplifying cardiovascular risks.
Medication-Specific Properties
The specific mechanism of action of an obesity medication significantly impacts its potential cardiac effects. For instance, medications that affect appetite regulation may influence heart rate and blood pressure in different ways compared to those that promote fat metabolism. The dosage, duration of use, and concurrent medications further influence the potential for adverse cardiac events. Pharmacokinetic factors, such as absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, also contribute to the individual response to the medication.
Drug Interactions
Interactions with other medications can significantly influence the cardiac effects of obesity medications. Some medications can increase the risk of cardiac events if taken concomitantly with obesity medications. For example, certain medications for hypertension or other cardiovascular conditions may potentiate the negative effects of obesity medications.
Lifestyle Factors
Patient lifestyle factors, such as diet, exercise, and smoking habits, influence the overall cardiovascular health and response to medications. A healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can mitigate the potential cardiac risks associated with obesity medications. Conversely, unhealthy lifestyle choices can exacerbate the effects, increasing the risk of adverse cardiovascular outcomes.
Table: Factors Influencing Cardiac Effects of Obesity Medications
| Factor | Medication Class Affected | Mechanism of Influence | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient Age | Most classes | Increased vulnerability in older adults due to decreased physiological reserve | Moderate |
| Pre-existing Cardiovascular Disease | Most classes | Underlying conditions can exacerbate medication-induced cardiac risks | High |
| Co-morbidities (e.g., Diabetes, Sleep Apnea) | Most classes | These conditions can interact with medication mechanisms, potentially increasing cardiac risk | Moderate to High |
| Medication Class | Specific to each class | Different mechanisms of action lead to varying cardiac effects | Variable |
| Dosage and Duration of Use | Most classes | Higher doses and longer durations can increase the potential for adverse events | Moderate to High |
| Drug Interactions | Most classes | Concurrent medications can alter the effects of obesity medications on the heart | Variable |
| Lifestyle Factors | Most classes | Healthy lifestyle choices can mitigate risks, while unhealthy choices can exacerbate them | Moderate |
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, the cardiac effects of obesity medications are a complex issue requiring careful consideration. While these medications can be effective in managing obesity, potential cardiac risks exist, and their severity varies depending on the medication class and individual factors. Further research is crucial to fully understand the nuances of these interactions. This comprehensive overview provides valuable insights into the potential impact of obesity medications on cardiovascular health, empowering readers to make informed decisions in consultation with healthcare professionals.

