Ringing in ears symptoms causes and treatment is a complex issue affecting many people. This comprehensive guide explores the various aspects of tinnitus, from understanding its different types and symptoms to exploring potential causes, diagnosis methods, and a range of treatment options. We’ll delve into lifestyle modifications and management strategies, including coping mechanisms and stress reduction techniques. Ultimately, this guide aims to provide a thorough understanding of tinnitus and empower readers with knowledge to navigate this often-challenging condition.
Understanding the nuances of tinnitus is crucial. From the subtle ringing to the more pronounced sensations, we’ll break down the various symptoms and their potential severity. Different causes contribute to this condition, from medical conditions to environmental factors and lifestyle choices. This exploration delves into the intricacies of tinnitus, highlighting the importance of proper diagnosis and effective treatment strategies.
Defining Ringing in Ears (Tinnitus)
Tinnitus, the perception of a sound in the ears when no external source is present, is a common and often frustrating condition. It’s a subjective experience, meaning it’s only heard by the person experiencing it. This can range from a mild buzzing to a loud, roaring sound, significantly impacting quality of life for those affected. Understanding the different types and characteristics of tinnitus is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment.This section delves into the specifics of tinnitus, from its varied presentations to the nuances of its perception.
We’ll examine the difference between subjective and objective tinnitus, discuss the common experiences across different populations, and analyze the diverse forms of this auditory phenomenon.
Definition of Tinnitus
Tinnitus is defined as the perception of sound in the absence of an external source. Crucially, it’s an auditory sensation, not a physical condition of the ear itself. The sound can manifest in various ways, including ringing, buzzing, hissing, clicking, or whistling. The intensity and type of sound can vary greatly from person to person, and even fluctuate over time for the same individual.
Subjective vs. Objective Tinnitus
A key distinction lies between subjective and objective tinnitus. Subjective tinnitus is the most common type, where the sound is only perceived by the person experiencing it. This is the type most people think of when they hear the term tinnitus. Objective tinnitus, on the other hand, is a sound that can be heard by a healthcare professional using a stethoscope.
This usually indicates an underlying physical condition, such as a vascular issue in the ear or jaw. It is less prevalent than subjective tinnitus.
Common Perceptions of Tinnitus Across Demographics
The perception of tinnitus varies across different demographics. While the experience of the sound itself is subjective, studies suggest that factors like age, gender, and even cultural background might play a role in how the condition is perceived and reported. For example, individuals in certain age groups might be more susceptible to experiencing tinnitus due to the natural physiological changes that occur with aging.
Furthermore, cultural influences can shape how people interpret and describe the auditory sensations associated with tinnitus. These perceptions can impact how individuals cope with and seek help for tinnitus.
Types of Tinnitus
Different types of tinnitus exist, each characterized by the nature of the sound perceived. Understanding these distinctions can aid in diagnosis and treatment planning.
| Type of Tinnitus | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Pulsatile Tinnitus | A throbbing or pulsing sound that often synchronizes with the heartbeat. | A rhythmic buzzing, or a sensation that feels like a heartbeat inside the ear. |
| Continuous Tinnitus | A constant sound that persists without interruption. | A consistent ringing or hissing sound. |
| Intermittent Tinnitus | A sound that comes and goes. | A buzzing sound that appears and disappears sporadically. |
| High-Pitched Tinnitus | A sound perceived as high-frequency, often described as a whistling or screeching sensation. | A high-pitched whine. |
| Low-Pitched Tinnitus | A sound perceived as low-frequency, often described as a rumbling or humming sensation. | A deep, low hum. |
Symptoms of Ringing in Ears
Tinnitus, the perception of a ringing sound in the ears, isn’t always just a simple buzzing. It can manifest in a complex array of symptoms, impacting not only auditory perception but also overall well-being. Understanding these diverse symptoms is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management.Beyond the ringing, tinnitus often presents with a range of accompanying sensations. These associated symptoms can vary significantly in their intensity and frequency, making it challenging to pinpoint the underlying cause.
Recognizing these broader symptoms is vital for comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plans.
Ever experienced ringing in your ears? It’s a common complaint, and understanding the causes and treatment options can be helpful. Tinnitus, as it’s medically known, can stem from various factors, including earwax buildup or exposure to loud noises. Fortunately, many cases can be managed effectively. But, the complex issue of healthcare systems is also relevant here, as access to quality care can vary significantly depending on the type of system in place.
This often leads to discussions about universal healthcare, a topic often confused with socialized medicine. Exploring the difference between the two is crucial for understanding how healthcare systems can influence access to treatments for conditions like tinnitus. For a deeper dive into the nuances of universal healthcare versus socialized medicine, check out this insightful article: is universal healthcare the same as socialized medicine.
Regardless of the system, proper diagnosis and treatment are key to managing tinnitus effectively.
Varied Intensity and Frequency of Tinnitus
The intensity of tinnitus can fluctuate greatly. Some individuals experience a faint, almost imperceptible ringing, while others describe a loud, intrusive sound that dominates their daily life. Similarly, the frequency with which tinnitus occurs can vary widely. It may be constant or intermittent, appearing and disappearing unpredictably. This variability adds complexity to diagnosis and treatment.
The unpredictable nature of the sound can significantly impact daily life.
Associated Symptoms
Tinnitus isn’t isolated to the ears. It frequently co-occurs with other symptoms that affect overall health and well-being. These include, but aren’t limited to:
- Headaches: A common complaint, headaches associated with tinnitus can range from mild tension headaches to more severe migraines. The pain may be localized or diffuse, and its intensity can correlate with the severity of the tinnitus.
- Dizziness: Vertigo, or a feeling of spinning or imbalance, is another frequent companion to tinnitus. This can be debilitating, affecting balance and coordination, leading to falls or difficulty performing everyday tasks.
- Sleep Disturbances: Tinnitus can disrupt sleep patterns. The constant sound can make it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep, leading to fatigue and impacting daytime functioning. Many patients report difficulty concentrating or experiencing mood swings due to the sleep deprivation.
- Anxiety and Depression: The chronic nature of tinnitus and the associated symptoms can trigger anxiety and depression. The inability to control the sound can lead to feelings of stress and isolation.
- Concentration Issues: The constant sound can make it difficult to concentrate on tasks, leading to difficulties at work or school. This impact is more significant for those in demanding jobs or educational settings.
Severity Levels of Tinnitus Symptoms
The following table provides a general overview of common tinnitus symptoms and their potential severity levels. It’s crucial to remember that this is not a diagnostic tool and individual experiences can vary greatly. Consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and treatment.
| Symptom | Mild | Moderate | Severe |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ringing Intensity | Faint, intermittent | Moderate, noticeable | Loud, constant, overwhelming |
| Associated Headaches | Occasional, mild tension | Frequent, moderate pain | Severe, migraine-like pain |
| Dizziness/Vertigo | Occasional lightheadedness | Moderate, affects balance | Severe, debilitating, causes falls |
| Sleep Disturbances | Minor sleep disruption | Significant sleep impairment | Inability to sleep, severe fatigue |
Causes of Ringing in Ears
Tinnitus, the perception of a ringing, buzzing, or hissing sound in the ears, can have a variety of underlying causes. Understanding these causes is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. This isn’t always straightforward, as sometimes the cause can be elusive. Pinpointing the source of the ringing can significantly impact the approach to management.The causes of tinnitus can be broadly categorized into medical conditions, lifestyle factors, and environmental exposures.
The interplay of these factors can contribute to the development and severity of tinnitus. Age also plays a role, as certain conditions become more prevalent with advancing years. It’s essential to remember that not all cases of tinnitus have a clear-cut identifiable cause.
Medical Conditions
Numerous medical conditions can lead to tinnitus. These conditions can affect the inner ear, the auditory nerve, or other parts of the nervous system. For instance, hearing loss, often associated with aging, can contribute to tinnitus. Additionally, cardiovascular issues can influence the flow of blood to the inner ear, potentially impacting its function and leading to tinnitus.
- Hearing loss (presbycusis, noise-induced hearing loss, otosclerosis): Age-related hearing loss (presbycusis) is a common contributor. Exposure to loud noises can also cause permanent damage, resulting in tinnitus and hearing loss. Otosclerosis, a bone growth disorder, can affect the middle ear, sometimes leading to hearing loss and tinnitus.
- Ear infections (otitis media, otitis externa): Infections in the middle ear (otitis media) or outer ear (otitis externa) can lead to inflammation and damage that can cause tinnitus.
- Meniere’s disease: This inner ear disorder can cause vertigo, hearing loss, and tinnitus. Symptoms can vary in severity and frequency.
- Acoustic neuroma: A benign tumor on the auditory nerve can cause hearing loss and tinnitus.
- Vascular disorders: Conditions affecting blood flow to the inner ear, like hypertension, can sometimes cause tinnitus. Examples include narrowing of blood vessels or blockage.
- Certain medications: Some medications, particularly those used to treat high blood pressure, can cause tinnitus as a side effect.
- TMJ (temporomandibular joint) disorders: Problems with the jaw joint can sometimes manifest as tinnitus.
- Head and neck injuries: Traumatic head injuries can affect the auditory system, potentially leading to tinnitus.
- Neurological conditions (e.g., multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease): Neurological disorders can sometimes cause tinnitus due to the impact on the nervous system.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle choices can significantly influence the risk of developing or exacerbating tinnitus.
- Stress: Chronic stress can affect the nervous system and potentially contribute to or worsen tinnitus.
- Poor diet: A diet lacking essential nutrients might indirectly affect the health of the inner ear, which can influence tinnitus. An example could be a diet low in vitamins and minerals.
- Lack of sleep: Insufficient sleep can lead to increased stress hormones, which can exacerbate existing tinnitus or contribute to its development.
- Smoking: Smoking can damage the inner ear and blood vessels, potentially contributing to tinnitus.
Environmental Factors
Environmental exposures can also contribute to the development of tinnitus.
- Noise exposure: Prolonged or intense exposure to loud noises (e.g., construction sites, concerts, machinery) is a leading cause of noise-induced hearing loss, a common trigger for tinnitus.
- Chemical exposure: Certain chemicals, present in the workplace or environment, can affect the inner ear and lead to tinnitus. An example could be exposure to certain solvents or heavy metals.
Hearing Loss and Tinnitus
A strong link exists between hearing loss and tinnitus. Often, hearing loss can be a contributing factor to or a symptom of underlying conditions that lead to tinnitus.
- Hearing loss is often a key factor in the development of tinnitus, particularly in cases of age-related hearing loss.
- Conversely, tinnitus can sometimes precede or accompany hearing loss, suggesting a common underlying cause.
Diagnosing Ringing in Ears: Ringing In Ears Symptoms Causes And Treatment
Pinpointing the cause of tinnitus, or ringing in the ears, is crucial for effective treatment. The diagnostic process often involves a multifaceted approach, combining patient history, physical examinations, and various tests to determine the underlying cause. This process aims to differentiate between treatable medical conditions and the more challenging cases where tinnitus is a symptom of a complex condition.The diagnostic journey for tinnitus starts with a thorough evaluation of the patient’s medical history.
This includes inquiries about potential contributing factors such as medication use, exposure to loud noises, ear infections, and other health conditions. The doctor will also assess the characteristics of the ringing, such as its pitch, loudness, and duration, to gain a better understanding of the potential source.
Initial Assessments and Examinations
A crucial first step in diagnosing tinnitus involves a comprehensive medical history. This includes questions about potential contributing factors, like medication use, exposure to loud noises, ear infections, or other health issues. Furthermore, the physician will carefully evaluate the patient’s overall health and any other symptoms present. This is often followed by a physical examination of the ears, nose, and throat (ENT examination).
The doctor will use an otoscope to visually inspect the ear canal and eardrum for any visible abnormalities or signs of infection. This physical examination helps rule out obvious causes such as impacted earwax or infections.
Methods for Determining Underlying Causes
Pinpointing the specific cause of tinnitus necessitates a range of diagnostic methods. These methods are designed to assess the auditory system, identify potential medical conditions, and rule out other possible sources. The selection of tests will vary depending on the patient’s symptoms and medical history.
Common Diagnostic Tools
Several tools are commonly used in the diagnostic process for tinnitus. These tools aid in identifying the source of the ringing and help direct treatment strategies.
- Audiometry: This crucial test assesses the patient’s hearing sensitivity across various frequencies. Abnormal hearing thresholds can suggest underlying ear conditions contributing to tinnitus. For instance, hearing loss can often accompany tinnitus, highlighting a potential connection between the two.
- Tympanometry: This test measures the movement and pressure within the middle ear. It helps identify any abnormalities in the eardrum or middle ear structures that might be causing or contributing to tinnitus.
- Acoustic Reflex Testing: This test measures the response of the middle ear muscles to sound. Anomalies in the acoustic reflex can point to problems in the auditory pathway.
- MRI or CT Scan: In cases where structural abnormalities in the brain or inner ear are suspected, an MRI or CT scan can be employed to visualize these areas and rule out conditions like tumors or vascular malformations.
- Blood Tests: These tests can help identify underlying medical conditions that might be contributing to tinnitus. For example, some blood tests can detect metabolic imbalances or infections that might be related to the ringing in the ears.
Diagnostic Tests and Purposes
The following table Artikels common diagnostic tests and their respective purposes in the evaluation of tinnitus:
| Diagnostic Test | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Audiometry | Evaluates hearing sensitivity across various frequencies. |
| Tympanometry | Assesses middle ear function and pressure. |
| Acoustic Reflex Testing | Measures middle ear muscle response to sound. |
| MRI/CT Scan | Identifies structural abnormalities in the brain or inner ear. |
| Blood Tests | Identifies underlying medical conditions. |
Treatment Options for Ringing in Ears
Dealing with tinnitus, the persistent ringing or buzzing in the ears, can be frustrating. Fortunately, a range of treatment options are available, from medication and therapy to lifestyle modifications. Finding the right approach often involves a personalized strategy tailored to the individual’s specific needs and the underlying cause of the tinnitus.Understanding the different treatment approaches is crucial for effectively managing tinnitus.
Not all treatments are equally effective for everyone, and the best course of action may vary significantly depending on the type of tinnitus and its underlying causes. Some treatments focus on alleviating the symptoms, while others aim to address the root cause, potentially leading to long-term relief.
Medication Approaches
Many medications can potentially help manage tinnitus, though not all are directly aimed at the ringing itself. Some medications can help address the underlying medical condition contributing to tinnitus, while others can help manage associated symptoms like anxiety or depression, which can exacerbate tinnitus perception. The effectiveness of these medications varies considerably from person to person. Consult a physician to determine the suitability and potential risks of medication for tinnitus.
Therapy-Based Treatments
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and other therapies are becoming increasingly recognized for their potential to manage tinnitus. CBT helps individuals understand and change negative thought patterns related to tinnitus, reducing the emotional distress it can cause. For instance, individuals might learn to reframe their perception of the ringing sound, making it less intrusive and less anxiety-provoking. Other therapies focus on relaxation techniques, mindfulness, and stress reduction, all of which can impact the experience of tinnitus.
Non-Medical Treatments
Numerous non-medical approaches can help manage tinnitus symptoms. Sound therapy, using specialized sound machines or apps, aims to mask the tinnitus sound with other sounds. Hearing aids can be beneficial for some individuals with tinnitus, particularly if it’s linked to hearing loss. White noise generators, for example, can mask the ringing sound, reducing its perceived intensity.
Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting healthy lifestyle choices can significantly influence tinnitus management. Adequate sleep, stress management techniques, and a balanced diet are all crucial. Avoiding excessive caffeine or alcohol consumption can also play a role in reducing the intensity of tinnitus symptoms. For example, someone experiencing tinnitus might find that stress reduction techniques, like yoga or meditation, are highly beneficial in managing the condition.
Comparison of Treatment Options
| Treatment Option | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Medication | Potentially addresses underlying conditions; manages associated symptoms. | Can have side effects; may not directly address tinnitus; effectiveness varies. |
| Therapy (e.g., CBT) | Addresses the psychological impact of tinnitus; helps manage stress and anxiety; promotes coping mechanisms. | May require multiple sessions; effectiveness can vary; doesn’t eliminate the sound itself. |
| Sound Therapy | Masks the tinnitus sound; provides distraction; relatively inexpensive. | May not be effective for everyone; requires consistent use; can be disruptive to others. |
| Hearing Aids | Can help improve hearing and potentially reduce tinnitus perception; suitable for certain cases. | Not suitable for all types of tinnitus; may not eliminate the sound; can be costly. |
| Lifestyle Modifications | Addresses overall well-being; can improve tinnitus management; relatively inexpensive and accessible. | May not be sufficient for all cases; requires commitment to changes; doesn’t directly address the tinnitus source. |
Management Strategies for Ringing in Ears
Living with tinnitus, the constant ringing or buzzing in the ears, can be challenging. While a cure isn’t always possible, effective management strategies can significantly improve quality of life. These strategies focus on coping mechanisms, stress reduction, and cognitive behavioral approaches. Understanding the role of these factors is crucial for individuals experiencing tinnitus.Managing tinnitus involves more than just addressing the sound itself; it necessitates a holistic approach that targets the psychological and emotional impact.
Effective strategies focus on reducing stress, improving coping mechanisms, and fostering a positive mindset.
Stress Reduction Techniques
Stress plays a significant role in exacerbating tinnitus symptoms. Chronic stress can heighten the perception of the ringing, making it more noticeable and bothersome. Implementing stress-reducing techniques is an important part of tinnitus management. These techniques can help to calm the nervous system, leading to a reduction in perceived tinnitus intensity.
- Mindfulness meditation involves focusing on the present moment without judgment. Practicing mindfulness can help to reduce stress and anxiety, which can in turn lessen the perception of tinnitus. Studies have shown that mindfulness meditation can help individuals better cope with the emotional distress associated with tinnitus.
- Deep breathing exercises are simple yet powerful tools for managing stress. Deep, slow breaths can calm the nervous system, lowering heart rate and blood pressure. This relaxation response can help reduce the intensity of tinnitus.
- Progressive muscle relaxation involves systematically tensing and relaxing different muscle groups. This technique helps to release physical tension and promote relaxation, which can reduce the perception of tinnitus.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for Tinnitus
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a type of psychotherapy that helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors. In the context of tinnitus, CBT can help individuals challenge negative thoughts and beliefs about their tinnitus.CBT helps individuals to reframe their perception of tinnitus. It helps them to recognize that the tinnitus, while present, does not necessarily control their lives.
By changing their thought processes, individuals can often reduce their anxiety and distress related to tinnitus.
Support Groups and Counseling
Support groups provide a valuable forum for sharing experiences and coping strategies with others who understand the challenges of living with tinnitus. The shared experience and support from peers can be immensely helpful in managing the emotional burden of tinnitus.Counseling can provide a safe and confidential space for individuals to explore the emotional impact of tinnitus. A counselor can offer guidance and support in developing coping mechanisms, addressing anxiety and depression, and promoting overall well-being.
Relaxation Techniques, Ringing in ears symptoms causes and treatment
Relaxation techniques can be invaluable in managing tinnitus symptoms. These techniques aim to calm the nervous system and reduce stress, leading to a decrease in the perceived intensity of tinnitus.
- Yoga combines physical postures, breathing techniques, and meditation to promote relaxation and stress reduction. Yoga can help individuals find balance and improve their overall well-being, which can positively impact tinnitus.
- Tai Chi involves slow, flowing movements that combine physical exercise with mindfulness. The meditative aspect of Tai Chi can help to reduce stress and improve focus, potentially decreasing the perception of tinnitus.
- Listening to calming music can be a powerful tool for relaxation. The gentle sounds and rhythms can help to soothe the mind and body, providing a sense of calm and reducing the perceived intensity of tinnitus.
Prevention of Ringing in Ears
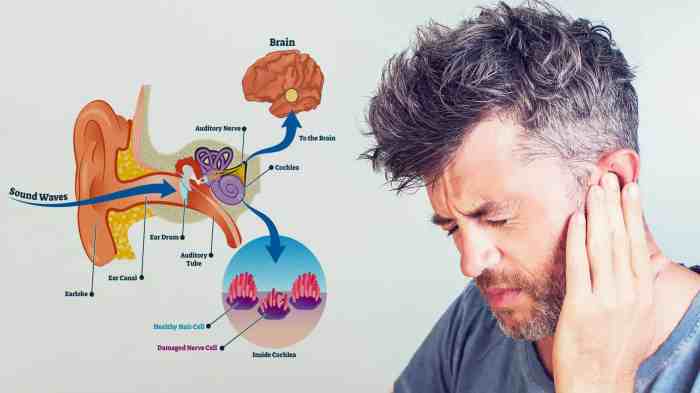
Tinnitus, the perception of ringing or buzzing sounds in the ears, can significantly impact quality of life. While often a symptom of an underlying condition, proactive measures can contribute to reducing the risk of developing tinnitus or mitigating its severity. Understanding the factors that contribute to tinnitus and implementing preventative strategies are crucial for managing this often-debilitating condition.Preventive strategies focus on protecting hearing health and adopting lifestyle choices that minimize the risk factors associated with tinnitus development.
Ever experienced ringing in your ears? It’s a common issue with various causes, from earwax buildup to more serious conditions like Meniere’s disease. Sometimes, lifestyle choices like stress or loud noises play a role. Interestingly, some people suggest using natural remedies like coconut oil for potential relief, though more research is needed. In fact, comparing coconut oil to olive oil for general health benefits is a popular topic.
This comparison might help understand the potential role of different fats in overall well-being coconut oil vs olive oil. Ultimately, consulting a doctor is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment of tinnitus.
These preventative measures, when combined with appropriate medical care if tinnitus arises, can empower individuals to take control of their auditory well-being.
Identifying Contributing Factors
Tinnitus can stem from a multitude of factors, some controllable, others not. Understanding these factors is crucial for developing effective preventative measures. These factors include exposure to loud noises, certain medications, ear infections, and underlying medical conditions.
Lifestyle Choices for Prevention
Adopting healthy habits plays a significant role in reducing the risk of tinnitus. These choices include maintaining a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, staying hydrated, and managing stress effectively.
Protecting Hearing Health
Protecting your hearing health is paramount in preventing tinnitus. Prolonged exposure to loud noises is a major contributor to hearing loss, a significant risk factor for tinnitus.
- Noise-Induced Hearing Loss: Exposure to loud noises, such as those from concerts, construction sites, or even prolonged use of headphones at high volumes, can damage the delicate hair cells in the inner ear, leading to hearing loss and potentially tinnitus. This damage is often gradual and initially may not be noticeable. A classic example is a musician who plays in loud bands, gradually developing tinnitus as a result.
- Protecting Hearing in Daily Life: Even everyday activities can contribute to noise exposure. Using headphones at high volumes for extended periods, attending loud events, or working in noisy environments can all increase the risk. Understanding these scenarios and adopting measures to reduce exposure are crucial.
Importance of Regular Hearing Check-ups
Regular hearing check-ups are essential for early detection of hearing problems. These check-ups can identify potential issues before they progress and cause significant hearing loss, potentially leading to tinnitus. Early intervention can often help mitigate the impact of hearing loss and associated tinnitus.
- Proactive Hearing Health: A hearing check-up allows healthcare professionals to assess hearing function and identify any underlying issues that could contribute to tinnitus development. This proactive approach allows for timely intervention, possibly preventing further damage and associated symptoms.
- Tracking Hearing Changes: Hearing health professionals can track changes in hearing over time, enabling the early detection of progressive hearing loss. This is especially important for individuals with a family history of hearing problems or those exposed to frequent loud noises.
Minimizing Exposure to Loud Noises
Minimizing exposure to loud noises is a key component of preventing tinnitus. Strategies include using earplugs or earmuffs in noisy environments, limiting headphone volume, and taking breaks from loud activities.
- Sound Level Awareness: Understanding the decibel levels of various sounds is essential. Using noise-level meters or apps can help determine if a particular sound is potentially harmful to hearing. Recognizing and understanding decibel levels can help individuals take preventative measures.
- Environment Management: When working or socializing in environments with loud noises, implementing measures to minimize exposure is crucial. This can involve using hearing protection, taking breaks from loud activities, or finding quieter alternatives.
Illustrative Case Studies (Examples)
Understanding tinnitus through real-life experiences is crucial for effective management. Case studies offer insights into the diverse presentation, causes, and treatment responses of this auditory phenomenon. By examining individual stories, we can better appreciate the complexity of tinnitus and tailor strategies to address its impact on patients’ lives.Case studies highlight the variability in tinnitus experiences. Factors such as the underlying cause, symptom severity, and individual coping mechanisms all influence the effectiveness of treatment plans.
They provide valuable data points for understanding the range of experiences and responses to tinnitus.
Case Study 1: Occupational Noise Exposure
This case study focuses on a 45-year-old factory worker who developed tinnitus after years of exposure to loud machinery. The patient described a persistent, high-pitched ringing in their left ear, initially mild but gradually intensifying over time. This worsening was accompanied by an increased sensitivity to sounds in general. The patient reported difficulty concentrating at work and reduced sleep quality.The initial diagnostic evaluation revealed hearing loss, consistent with the history of noise exposure.
Experiencing ringing in your ears, or tinnitus, can be a real pain. It’s often linked to things like age-related hearing loss or even stress. While there’s no one-size-fits-all cure, some people find relief through natural remedies. For instance, some research suggests that certain dietary changes, like incorporating apple cider vinegar into your diet, apple cider vinegar benefits might help with reducing inflammation, a possible contributor to tinnitus.
But remember, consulting a doctor is crucial for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan for tinnitus.
The treatment approach involved hearing protection measures, such as earplugs and earmuffs, to mitigate further damage. Sound therapy, including white noise machines and nature sounds, was employed to mask the tinnitus and provide some relief. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) was also recommended to help the patient manage stress and anxiety associated with the condition. The patient’s progress was monitored closely, and adjustments to the treatment plan were made as needed.
Case Study 2: Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss
A 30-year-old woman presented with sudden onset tinnitus and profound hearing loss in her right ear. The tinnitus was described as a roaring, pulsatile sound, seemingly synchronized with her heartbeat. She experienced dizziness and nausea, adding to her discomfort.The rapid onset of symptoms suggested a possible vascular issue or an autoimmune response. Extensive diagnostic testing, including blood tests and imaging studies, was conducted to rule out other potential causes.
Hearing aids and assistive listening devices were implemented to improve her communication and reduce the impact of hearing loss. Sound therapy and tinnitus retraining therapy (TRT) were considered to manage the tinnitus. The patient showed a gradual improvement in symptoms over several months, highlighting the importance of early intervention and comprehensive care in such cases.
Case Study 3: Ototoxic Medication
A 65-year-old patient experiencing a constant, low-pitched buzzing tinnitus in both ears reported taking certain medications for their high blood pressure. The buzzing sound had been a gradual development over the previous three months. The patient also reported a slight but noticeable decrease in their overall hearing sensitivity.The patient’s medical history revealed the use of ototoxic medications. The physician recommended a review of the patient’s medication regimen and the possibility of switching to alternative, less ototoxic drugs.
This adjustment, combined with sound therapy and lifestyle modifications (stress reduction techniques), led to a notable reduction in the tinnitus intensity and improved overall well-being.
Case Study Summary Table
| Patient Details | Symptoms | Causes | Treatment Approaches |
|---|---|---|---|
| 45-year-old factory worker | Persistent high-pitched ringing, increased sound sensitivity | Occupational noise exposure, hearing loss | Hearing protection, sound therapy, CBT |
| 30-year-old woman | Roaring, pulsatile tinnitus, hearing loss, dizziness, nausea | Sudden sensorineural hearing loss, possible vascular issue | Hearing aids, assistive listening, sound therapy, TRT |
| 65-year-old patient | Constant low-pitched buzzing, decreased hearing sensitivity | Ototoxic medication | Medication review, sound therapy, lifestyle modifications |
Resources and Support
Finding yourself grappling with tinnitus can be isolating. It’s crucial to remember you’re not alone and there’s support available. This section details reliable resources and support services to help you navigate this experience.Understanding the resources available can empower you to take proactive steps toward managing your tinnitus and improving your overall well-being.
Reliable Online Resources
Numerous websites offer valuable information and support for tinnitus sufferers. These platforms often provide educational materials, connect individuals with others experiencing similar challenges, and offer access to professionals.
- The National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD): The NIDCD is a reliable source of information about tinnitus, its causes, and available treatments. Their website provides detailed explanations, research updates, and links to other relevant resources. Their comprehensive approach helps clarify complex information.
- Hearing.org: This organization provides resources and information about hearing loss, which is often associated with tinnitus. Their insights can help you understand the interplay between these conditions and how they affect your overall well-being.
- The Tinnitus Association: This organization is dedicated to supporting individuals experiencing tinnitus. They offer a wealth of information, support groups, and educational materials, fostering a sense of community for those affected.
Support Groups and Communities
Connecting with others who understand your experience can be incredibly beneficial. Support groups provide a safe space to share experiences, ask questions, and find encouragement. These groups can offer invaluable insights and perspectives from individuals who have firsthand experience with tinnitus.
- Online Forums and Support Groups: Many online platforms, including dedicated tinnitus forums and social media groups, allow individuals to connect and share their experiences. These virtual communities can offer a sense of belonging and provide practical advice.
- Local Support Groups: Some areas have local support groups or meetings where individuals with tinnitus can connect in person. These gatherings foster a sense of community and allow for face-to-face interaction.
Organizations and Services
Various organizations provide support services, including counseling, advocacy, and educational programs. These services can assist in managing the emotional and psychological aspects of living with tinnitus.
| Organization/Service | Website/Contact Information |
|---|---|
| The Tinnitus Association | [Link to The Tinnitus Association Website] |
| Hearing Loss Association of America (HLAA) | [Link to HLAA Website] |
| [Name of a local tinnitus support group (if applicable)] | [Contact information for the local group] |
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, ringing in ears symptoms causes and treatment involves a multifaceted approach. From identifying the underlying causes to exploring various treatment options and management strategies, this guide provides a holistic perspective. Remember that managing tinnitus often requires a personalized strategy, combining medical interventions, lifestyle adjustments, and coping mechanisms. Seeking professional help is vital in navigating this condition effectively.
This guide offers a valuable starting point for understanding and addressing this often-misunderstood condition.