Biotin for hair growth is a topic of considerable interest, and for good reason. This exploration delves into the fascinating world of biotin, examining its role in supporting not only healthy hair but also overall bodily functions. We’ll uncover the science behind biotin’s impact on hair follicle health, analyze supplementation strategies, and explore factors that affect its effectiveness.
The journey begins now, as we uncover the secrets behind biotin’s potential to promote luscious locks.
This comprehensive guide will explore the mechanisms of biotin action on hair follicles, comparing its effects with other potential hair growth supplements. We’ll examine the scientific evidence surrounding biotin supplementation for hair growth, including potential benefits, limitations, and potential side effects. Furthermore, we’ll explore the importance of diet, lifestyle choices, and underlying health conditions in biotin absorption and effectiveness.
Introduction to Biotin and Hair Growth
Biotin, also known as vitamin B7, plays a crucial role in various metabolic processes within the human body. It’s a water-soluble vitamin essential for healthy cell function and is involved in numerous biochemical pathways, including those related to energy production and the synthesis of fatty acids, amino acids, and glucose. Understanding its role in these fundamental processes provides insight into its potential impact on overall health, including hair growth.Biotin’s participation in these metabolic pathways is critical for the maintenance of healthy tissues and organs, making it a vital component for overall well-being.
This includes the production of keratin, a protein crucial for hair structure, which further highlights its possible connection to hair growth. While it’s important to maintain a balanced diet rich in biotin-containing foods, there’s ongoing research to clarify the specific effects on hair growth.
Biotin’s Functions in the Body
Biotin is a coenzyme involved in a variety of crucial metabolic processes. It acts as a carrier of carbon dioxide in carboxylation reactions, impacting the synthesis of fatty acids, amino acids, and glucose. These processes are essential for the production of energy and the maintenance of healthy bodily functions.
Biotin’s Impact on Hair Follicle Health
Biotin is a key component in the synthesis of keratin, the primary structural protein of hair. This suggests a potential role in supporting hair follicle health and potentially hair growth. However, the exact mechanisms are still under investigation. The complex interactions within hair follicles are multifaceted and involve various other nutrients and factors, not just biotin.
| Biotin’s Functions | Impact on Hair Growth |
|---|---|
| Essential for the synthesis of fatty acids, amino acids, and glucose. | Keratin production, a key structural protein in hair, relies on biotin. Potential impact on hair follicle health, but further research is needed. |
| Acts as a coenzyme in carboxylation reactions, crucial for energy production. | Energy is required for the growth and maintenance of hair follicles. Biotin’s role in energy metabolism may indirectly support hair growth. |
| Involved in the synthesis of proteins and other vital molecules. | Biotin’s participation in protein synthesis is relevant to hair follicle development and maintenance. The impact on hair growth is not definitively established. |
Scientific Evidence on Biotin and Hair Growth
Numerous studies have investigated the potential link between biotin supplementation and hair growth. While some studies show a positive correlation, the evidence remains inconclusive. A lack of rigorous, large-scale, and long-term clinical trials hinders a definitive conclusion. Furthermore, the results often vary significantly, suggesting that other factors, such as genetics, overall health, and diet, play significant roles in hair growth.
Factors Influencing Hair Growth
It’s important to note that hair growth is a complex process influenced by a multitude of factors, including genetics, hormonal balance, overall health, and nutritional intake. While biotin may contribute to the process, it’s not a standalone solution for hair growth issues.
Biotin’s supposed hair-growth benefits are often touted, but sometimes the focus shifts to other health concerns. While biotin might be a helpful supplement for thicker, healthier hair, it’s also interesting to consider treatments like eye injections for AMD. Eye injections for AMD are a more direct approach to preserving vision. Ultimately, though, biotin for hair growth remains a popular topic for many seeking natural remedies and healthy hair care routines.
Mechanisms of Biotin Action on Hair Follicles: Biotin For Hair Growth
Biotin, a crucial water-soluble vitamin, plays a vital role in the health and growth of hair. Understanding its molecular mechanisms within hair follicles is key to appreciating its importance. This deeper dive into biotin’s actions will illuminate how it interacts with other nutrients to support healthy hair development.Biotin’s impact on hair follicles extends beyond simply being a component in hair structure.
It is intricately involved in the metabolic processes that underpin hair growth, particularly the synthesis of keratin, the protein that forms the structural basis of hair. This influence extends to the overall health of the hair follicle, influencing its ability to produce strong, healthy hair.
Biotin and Keratin Synthesis
Keratin, the fundamental protein of hair, nails, and skin, relies on specific enzymatic processes for its formation. Biotin acts as a crucial coenzyme for these processes, particularly in the carboxylation reactions that are essential steps in keratin synthesis. The carboxylation reactions involve the addition of carboxyl groups to certain amino acids, modifying their structure and thus influencing the final keratin structure.
This modified keratin structure, directly influenced by biotin, contributes to the strength and resilience of the hair.
Interactions with Other Nutrients
Biotin’s action on hair follicles is not isolated; it interacts with other essential nutrients. For example, adequate protein intake is paramount. Proteins, the building blocks of keratin, need sufficient amounts to support the creation of robust and healthy hair. Furthermore, vitamins like vitamin A and vitamin C also contribute to the overall health of the hair follicle.
These vitamins contribute to collagen synthesis, blood circulation, and antioxidant defense, all of which indirectly support hair follicle function and health.
Biotin’s Influence on Hair Follicle Development
Biotin’s impact on hair follicle development is significant. It influences the proliferation and differentiation of cells within the hair follicle, creating a supportive environment for hair growth. The improved function of hair follicles results in stronger and healthier hair. This influence is seen through the activation of specific genes and pathways related to hair follicle cycling and maintenance.
For instance, research suggests that biotin may help regulate the hair growth cycle, ensuring consistent and healthy hair growth.
Comparison of Biotin with Other Hair Growth Supplements
| Supplement | Potential Mechanisms | Potential Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Biotin | Essential for keratin synthesis, influences hair follicle development. | Effectiveness can vary, and may need to be taken in conjunction with other nutrients. |
| Vitamin D | Plays a role in cell growth and differentiation, potentially impacting hair follicle health. | Effectiveness varies depending on individual vitamin D levels and may need to be supplemented with other nutrients. |
| Collagen Supplements | Supports hair follicle health, may contribute to hair strength. | Limited evidence on its direct impact on hair follicle health, may require supplementation with other nutrients. |
Biotin Supplementation for Hair Growth
Biotin, also known as vitamin B7, has garnered significant attention for its potential role in promoting hair growth. While it plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, its specific impact on hair follicle health and subsequent hair growth remains a subject of ongoing research. This section delves into the existing evidence surrounding biotin supplementation for hair growth, examining potential benefits, limitations, dosage forms, and potential side effects.
Summary of Research on Biotin and Hair Growth
Research on biotin’s effect on hair growth is multifaceted, with some studies showing positive results, while others offer less conclusive findings. The effectiveness of biotin supplementation for hair growth is not uniformly supported by high-quality, controlled trials. A significant portion of the existing research comes from observational studies or small-scale trials, limiting the strength of conclusions.
Potential Benefits and Limitations of Biotin Supplements
Biotin supplements may offer some benefits in addressing hair concerns, particularly in individuals with biotin deficiencies. However, the extent of these benefits and the specific mechanisms remain areas of active investigation. One potential benefit lies in the support of healthy hair follicle function. Limitations include the inconsistent findings across different studies and the lack of large-scale, long-term trials.
Furthermore, the perceived benefits might be subjective and influenced by factors like individual response and underlying health conditions. Individual experiences vary, highlighting the complexity of the issue.
Biotin Dosage Forms and Efficacy
Biotin is available in various dosage forms, including capsules, tablets, and liquids. The efficacy of these forms typically relies on the amount of biotin contained within the supplement. Precise dosage recommendations are dependent on individual needs and health conditions. Current research suggests that higher dosages may not always translate to improved hair growth results compared to lower dosages.
Further investigation into optimal dosages is necessary.
Possible Side Effects and Interactions
Potential side effects of biotin supplementation are generally mild and include digestive issues such as gas or bloating. Rarely, more serious adverse effects may occur. It’s crucial to note that biotin can interact with certain medications, potentially affecting their absorption or efficacy. Consulting a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement, especially if taking other medications, is strongly recommended.
Interactions with anticoagulants, for example, require careful consideration.
Studies on Biotin Supplementation
| Study | Dosage (mg/day) | Duration (weeks/months) | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Study 1 (Example) | 5 mg | 12 weeks | Minor improvements in hair growth reported by some participants; no significant difference from placebo in others. |
| Study 2 (Example) | 2.5 mg | 24 weeks | Statistically significant improvement in hair thickness and growth in a small sample size. |
| Study 3 (Example) | 1 mg | 6 months | No noticeable change in hair growth compared to placebo. |
| Study 4 (Example) | 10 mg | 18 weeks | Significant improvements in hair density reported by participants; larger study needed to confirm results. |
Note: The above table provides examples and should not be interpreted as a definitive list of all research findings. Further research is needed to fully understand the impact of biotin supplementation on hair growth. The outcomes in each study can be influenced by several factors, including participant demographics, study design, and the specific biotin preparation used.
Factors Affecting Biotin Uptake and Effectiveness
Biotin, a crucial B vitamin, plays a vital role in various bodily functions, including hair growth. While biotin supplementation can potentially support hair health, its effectiveness isn’t universal. Several factors influence the body’s ability to absorb and utilize biotin, impacting its overall impact on hair growth. Understanding these factors is essential for maximizing the potential benefits of biotin.Effective biotin absorption and utilization hinges on a combination of dietary choices, lifestyle factors, and underlying health conditions.
Factors such as the presence of other nutrients, interactions with medications, and pre-existing health conditions can either enhance or impede biotin’s efficacy. This complex interplay highlights the need for a holistic approach to consider when aiming to optimize biotin’s impact on hair health.
Dietary Influences on Biotin Absorption
Diet significantly impacts biotin absorption. A balanced diet rich in various food groups often provides adequate biotin intake. A diet deficient in specific nutrients can hinder biotin absorption, while a diet high in certain components can enhance it.
- Biotin-Rich Foods: A variety of foods naturally contain biotin. These include egg yolks, nuts, seeds, and leafy green vegetables. Consuming a diverse range of these foods can contribute to a healthy biotin intake.
- Fiber Intake: A high-fiber diet can sometimes hinder biotin absorption. Soluble fiber can bind to biotin, reducing its bioavailability. However, a moderate intake of fiber is essential for overall health. A balanced approach is key to optimizing biotin utilization.
- Anti-nutrients: Certain dietary components can interfere with biotin absorption. For example, excessive consumption of raw eggs may contain avidin, a protein that binds to biotin and prevents its absorption. Cooking eggs thoroughly can reduce this interaction.
Lifestyle Choices and Biotin Effectiveness
Lifestyle choices can also affect biotin uptake and utilization. Stress, for instance, can impact nutrient absorption and utilization. Adequate sleep and regular exercise are important for overall health and can contribute to improved nutrient utilization.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can impact the body’s ability to absorb and utilize nutrients, potentially affecting biotin’s effectiveness. Stress management techniques like exercise, meditation, or yoga can help mitigate these negative effects. Chronic stress can influence hormone levels, potentially affecting nutrient metabolism and absorption.
- Hydration: Adequate hydration is crucial for many bodily functions, including nutrient absorption. Maintaining proper hydration levels can support biotin’s bioavailability. Dehydration can impact the body’s ability to transport and utilize nutrients.
- Smoking: Smoking can affect nutrient absorption and utilization. Smoking can reduce nutrient bioavailability and potentially affect biotin’s effectiveness. Quitting smoking can have a positive impact on overall health, potentially improving nutrient absorption.
Interactions with Other Substances
Certain medications, supplements, or other substances can interact with biotin, affecting its absorption and effectiveness. These interactions can either increase or decrease biotin’s bioavailability. It is essential to discuss any potential interactions with a healthcare professional before supplementing with biotin.
- Medications: Some medications can interact with biotin, either enhancing or inhibiting its absorption. These interactions can affect the efficacy of the medication or biotin. Consulting a doctor is crucial to assess potential interactions.
- Supplements: Taking biotin alongside other supplements can lead to interactions. For instance, high doses of certain minerals or vitamins might affect biotin absorption. A balanced approach to supplement intake is crucial.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Certain underlying health conditions can affect nutrient absorption and utilization, potentially impacting biotin’s effectiveness. For example, malabsorption syndromes can reduce the body’s ability to absorb biotin. Individuals with such conditions should consult their healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage and approach.
Key Dietary Sources of Biotin
Biotin is naturally present in various foods. A diverse diet including these sources can contribute to a sufficient intake.
- Eggs: Egg yolks are excellent sources of biotin.
- Liver: Organ meats like liver are rich in biotin.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, cashews, and sunflower seeds are good sources of biotin.
- Legumes: Beans and lentils are valuable sources of biotin.
- Leafy Green Vegetables: Spinach, kale, and other leafy greens provide a small amount of biotin.
- Mushrooms: Mushrooms contain some biotin.
- Other sources: Other foods like sweet potatoes, avocados, and whole grains also contribute to biotin intake.
Comparison with Other Hair Growth Strategies
Biotin, while a promising supplement for hair health, isn’t a magic bullet. Understanding its effectiveness alongside other hair growth methods is crucial for a holistic approach. Different strategies target various aspects of hair follicle health, and a comprehensive strategy often involves combining multiple approaches for optimal results.Effective hair growth isn’t solely dependent on one factor; a combination of internal and external care often yields the best outcomes.
Biotin is often touted as a hair growth hero, but what about other options? For example, understanding how Rogaine minoxidil works for hair growth how rogaine minoxidil works for hair growth can provide a more complete picture. While biotin might support healthy hair follicles, Rogaine directly targets blood flow and hair follicle activity. Ultimately, exploring different approaches like biotin or Rogaine can help you find the best strategy for your hair growth journey.
This comparison delves into the strengths and weaknesses of biotin supplementation alongside topical treatments and lifestyle modifications to provide a more complete picture.
Effectiveness of Biotin Compared to Topical Treatments
Biotin’s primary mechanism is internal, influencing hair follicle health from within. Topical treatments, on the other hand, directly address the hair shaft and scalp. While biotin may improve the overall health of the hair follicle, its impact on the hair shaft itself is limited. Topical treatments like minoxidil or retinoids, for example, can stimulate hair growth directly on the scalp, but they often come with potential side effects and require consistent use for noticeable results.
A key difference lies in the speed of action; topical treatments can potentially show results sooner, but biotin’s effects might be more gradual and long-term.
Effectiveness of Biotin Compared to Lifestyle Changes, Biotin for hair growth
Lifestyle factors like stress, diet, and sleep play significant roles in hair health. Biotin supplementation can contribute to better hair growth by supporting healthy follicle function, but it doesn’t address the underlying causes of hair loss related to these factors. For instance, stress management techniques or dietary adjustments can have profound impacts on hair health, but these lifestyle changes require consistent effort over time.
A balanced approach often combines biotin supplementation with healthy habits to maximize its benefits.
Synergistic Effects of Combining Strategies
Combining biotin supplementation with other strategies can amplify their effects. For example, a balanced diet rich in proteins, vitamins, and minerals, coupled with biotin, can promote healthy hair growth from within. Similarly, incorporating topical treatments with a biotin regimen might target both the scalp and the follicle, creating a synergistic effect. The key lies in understanding the unique contributions of each approach and how they complement one another.
Key Differences Summary
Biotin supplementation primarily focuses on internal follicle health, while topical treatments directly address the hair shaft and scalp. Lifestyle changes, including diet and stress management, support the overall environment for hair growth. Combining strategies can create a synergistic effect, leading to more comprehensive hair health improvements.
Biotin’s supposed hair-growth benefits are often touted online, but it’s important to remember that its effects on conditions like hair loss aren’t always straightforward. While some find it helpful, it’s crucial to understand that biotin doesn’t treat serious neurological conditions like amyotrophic lateral sclerosis ALS, a progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis ALS requires specialized medical care and treatment plans, and biotin supplementation shouldn’t be used as a replacement for professional medical guidance. Ultimately, if you’re experiencing hair loss or concerns about your health, consulting a doctor is the best first step, whether you’re considering biotin or not.
Potential Benefits Beyond Hair Growth
Biotin, a crucial B vitamin, plays a significant role in various bodily functions. While its impact on hair growth is well-documented, its benefits extend beyond healthy tresses. Understanding its broader effects on overall health, especially in relation to hair, provides a more comprehensive picture of this essential nutrient.Biotin’s influence extends beyond hair follicle health to encompass energy production and metabolic function.
It’s an important player in the processes that transform food into usable energy, impacting the body’s ability to utilize carbohydrates, fats, and proteins efficiently. This impact can contribute to maintaining a healthy weight and promoting energy levels. The synergy between proper biotin intake and hair health highlights the interconnectedness of nutritional components in supporting overall well-being.
Broader Impact on Overall Health
Biotin’s influence on overall health, while not as prominently featured as its hair-growth benefits, is still significant. It’s essential for the synthesis of several proteins, including those involved in cell growth, repair, and energy production. These proteins contribute to maintaining healthy skin and nails, and while hair is often the primary focus, biotin supports these structures too. Furthermore, adequate biotin levels can support a healthy nervous system, which in turn contributes to cognitive function and overall well-being.
Biotin’s Role in Energy Production and Metabolic Function
Biotin is a critical coenzyme in various metabolic processes, facilitating the conversion of food into energy. This role contributes to a stable energy level throughout the day, preventing energy crashes and maintaining a steady metabolic rate. The impact on energy levels can be particularly noticeable in individuals who may be deficient in biotin, or have dietary restrictions affecting their intake of this essential vitamin.
Documented Health Risks of Excessive Biotin Intake
While biotin is generally considered safe, excessive intake can lead to potential health concerns. High doses of biotin supplements can interfere with the absorption of other B vitamins, leading to imbalances in the body’s nutritional profile. Moreover, excessive intake may cause mild side effects like nausea or digestive discomfort. It’s important to note that these side effects are usually mild and temporary.
However, consulting a healthcare professional is always recommended for any concerns related to supplement use.
Summary of Biotin Benefits
- Improved Hair Growth and Health: Biotin plays a crucial role in keratin synthesis, directly impacting hair follicle health, promoting stronger, healthier hair, and preventing hair loss.
- Enhanced Energy Levels: Biotin is involved in metabolic processes, converting food into usable energy, contributing to sustained energy levels throughout the day.
- Support for Healthy Skin and Nails: Beyond hair, biotin supports healthy skin and nail growth and strength by participating in protein synthesis.
- Metabolic Function Support: Biotin’s role as a coenzyme in converting food into energy supports efficient metabolic processes, promoting healthy weight management.
- Potential for Neurological Function: Adequate biotin levels might contribute to a healthy nervous system, potentially supporting cognitive function and overall well-being.
- Important Note: Excessive intake might cause minor digestive issues or interfere with the absorption of other B vitamins.
Understanding Hair Loss and Biotin
Hair loss, a common concern for many, can stem from various factors, both internal and external. Understanding these causes and how biotin might (or might not) play a role is crucial for anyone considering biotin supplementation for hair health. This section will delve into the different types of hair loss, their potential triggers, and biotin’s possible role in addressing them.
Types of Hair Loss and Potential Causes
Hair loss isn’t a single entity; it manifests in various forms, each with potential contributing factors. Recognizing these distinctions is important for targeted interventions, including considering biotin’s potential benefits. Different types of hair loss include:
- Androgenetic Alopecia (Male and Female Pattern Baldness): This is the most common type of hair loss, predominantly influenced by genetic factors and hormonal changes. Dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone, shrinks hair follicles, leading to miniaturization and eventual hair loss. While biotin may support overall hair health, its effectiveness in reversing established pattern baldness is limited.
- Telogen Effluvium: This type of hair loss occurs when a large number of hair follicles enter the resting phase (telogen) simultaneously. This can be triggered by significant stress, illness, surgery, dietary deficiencies, or hormonal changes. Biotin, due to its role in supporting healthy hair growth, may be beneficial in supporting hair regrowth during recovery from telogen effluvium.
- Alopecia Areata: This autoimmune disorder causes patchy hair loss. The exact cause isn’t fully understood, but it’s believed to involve the immune system attacking hair follicles. Biotin’s role in this type of hair loss is not well-established and further research is needed to determine its effectiveness.
- Traction Alopecia: This type of hair loss arises from constant tension or pulling on the hair, such as from tight hairstyles. Biotin is unlikely to directly address this type of hair loss, as the issue lies in the physical stress to the hair follicle, not necessarily in nutritional deficiencies.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Beyond biotin, various nutritional deficiencies can contribute to hair loss. Iron deficiency, protein deficiency, and deficiencies in other essential vitamins and minerals can all negatively impact hair health. Biotin may be a part of a comprehensive approach to addressing nutritional deficiencies contributing to hair loss.
Biotin’s Potential Role in Hair Growth
While biotin is essential for healthy hair growth, its effectiveness in addressing different types of hair loss varies. It plays a crucial role in keratin synthesis, a protein essential for hair structure. Therefore, sufficient biotin intake may support hair health.
- Androgenetic Alopecia: Current evidence does not support biotin’s effectiveness in reversing or preventing the progression of this genetically-driven hair loss. However, it may contribute to supporting overall hair health in individuals with this condition.
- Telogen Effluvium: Biotin may be helpful in supporting the transition back to the growth phase in cases of telogen effluvium, especially when combined with addressing the underlying causes like stress or nutritional deficiencies.
- Alopecia Areata: Further research is needed to determine the potential impact of biotin on alopecia areata. Biotin supplementation may not be a primary treatment but may be part of a holistic approach.
- Traction Alopecia: Biotin will not reverse traction alopecia. The key to addressing this type of hair loss lies in reducing the physical stress on the hair.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Biotin supplementation can be a component of a broader approach to addressing underlying nutritional deficiencies that may contribute to hair loss. It may aid in supporting hair growth when combined with addressing the underlying cause.
Hair Growth Cycle Stages
Understanding the hair growth cycle is vital to appreciating the factors that influence hair loss and growth. The cycle is characterized by three stages:
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Anagen | Active growth phase. Hair follicle actively produces hair. |
| Catagen | Transitional phase. Hair follicle shrinks, and hair production slows down. |
| Telogen | Resting phase. Hair follicle is dormant, and hair is shed. |
The diagram below illustrates the hair growth cycle. [Diagram would be presented here but cannot be created within the current text format].
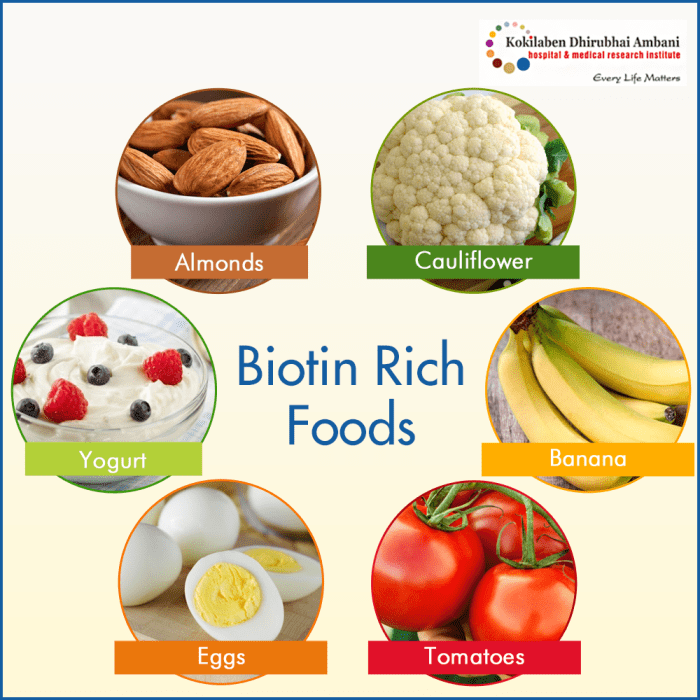
Biotin-Rich Foods and Dietary Recommendations

Biotin, a vital B vitamin, plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including hair growth. While biotin supplements are readily available, incorporating biotin-rich foods into your diet is often a more sustainable and natural approach. This method allows your body to absorb biotin gradually, mimicking its natural process. A balanced diet rich in biotin, along with other essential nutrients, contributes to overall health and well-being, fostering healthy hair and more.
Biotin-Rich Food Sources
A diverse range of foods are excellent sources of biotin. These foods provide the necessary nutrients for optimal hair health, alongside other benefits for overall health. A varied diet encompassing these foods is often more effective than relying solely on supplements.
- Eggs: A complete protein source, eggs are rich in biotin and other essential nutrients like protein and vitamins. They contribute significantly to a balanced diet and are an excellent source of biotin for hair growth.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent sources of biotin. They are also rich in fiber and protein, promoting digestive health and providing sustained energy. The inclusion of these foods in a balanced diet enhances biotin intake.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, pumpkin seeds, and sunflower seeds are packed with biotin, healthy fats, and other essential nutrients. Incorporating these into snacks and meals contributes to a balanced and biotin-rich diet.
- Sweet Potatoes: These root vegetables are not only rich in biotin but also in vitamins, minerals, and fiber. They are a great source of carbohydrates, promoting overall energy levels.
- Avocados: Known for their healthy fats, avocados also contain a decent amount of biotin. They add creaminess and healthy fats to various dishes, making them a great addition to a biotin-rich diet.
- Broccoli: This cruciferous vegetable is a good source of biotin and other beneficial nutrients. It is a versatile vegetable, which can be incorporated into salads, stir-fries, or roasted dishes.
- Mushrooms: Certain types of mushrooms, like shiitake and oyster mushrooms, contain a notable amount of biotin. They are a good source of minerals and can be added to various dishes for a more nutritious meal.
Importance of Balanced Diet for Biotin Absorption
Biotin absorption isn’t solely dependent on the amount of biotin-rich foods consumed. Other nutrients play a critical role in the efficient absorption of biotin from the diet. A balanced diet ensures the presence of these supporting nutrients.
- Protein: Adequate protein intake is essential for the body’s overall functions, including the production of hair keratin. Proteins contribute to the structure and strength of hair follicles.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Several vitamins and minerals are crucial for the body’s metabolic processes and the health of the hair follicles. These include vitamin C, vitamin E, and zinc. A diet rich in a variety of fruits and vegetables ensures a good supply of these nutrients.
- Healthy Fats: Essential fatty acids are vital for hair health. Incorporating foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids (e.g., fatty fish, flaxseeds) contributes to a healthy scalp and hair.
Sample Biotin-Rich Diet Plan
This is a sample daily plan, which can be adjusted based on individual needs and preferences.
| Meal | Description | Biotin Source(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Breakfast | Oatmeal with berries, nuts, and seeds | Oatmeal, nuts, seeds, berries |
| Lunch | Lentil soup with a side salad | Lentils, leafy greens |
| Dinner | Baked salmon with roasted broccoli and sweet potatoes | Salmon, broccoli, sweet potatoes |
| Snacks | Avocado toast, a handful of almonds, or a serving of pumpkin seeds | Avocado, almonds, pumpkin seeds |
Healthy Eating Plan for High Biotin Content
A balanced diet is crucial for optimal biotin intake and absorption. Prioritize whole, unprocessed foods, focusing on a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. This dietary approach provides the body with a wide range of essential nutrients and supports overall health.
Ending Remarks

In conclusion, biotin’s potential to support hair growth is a compelling area of research. While it may not be a miracle cure for all hair loss concerns, understanding its mechanisms, potential benefits, and limitations is crucial for informed decision-making. This discussion highlights the importance of a holistic approach, considering factors like diet, lifestyle, and underlying health conditions, alongside the potential for combining biotin with other hair growth strategies.
Ultimately, the choice to incorporate biotin into your hair care routine should be a personal one, made after careful consideration and consultation with a healthcare professional.